OpenStax Microbiology Test Bank Chapter 2: How We See the Invisible World
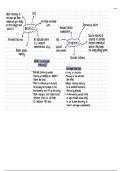
OpenStax Microbiology Test Bank Chapter 2: How We See the Invisible World * = Correct answer Multiple Choice 1. Which term is used to refer to a wave’s rate of vibration? A. amplitude B. frequency* C. trough D. wavelength 2. On the figure, which letter represents a refracted ray of light? A. A B. B C. C D. D* 3. On the electromagnetic spectrum, which type of wave has the shortest wavelength? A. cosmic ray* B. infrared ray C. ultraviolet ray D. visible light 4. Dyes are often used during microscopy to increase which of the following? A. contrast* B. magnification C. motility D. resolution 5. Which of the following was the first to use the term “cells”? A. Robert Hooke* B. Robert Koch C. Carolus Linnaeus D. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 6. Which of the following is the typical magnification of an object viewed using a 10× ocular lens and a 100× objective lens on a brightfield microscope? A. 1× B. 10× C. 100× D. 1000×* 7. Most modern microscopes have two eyepieces, meaning that they are which of the following? A. binocular* B. monocular C. oil immersion D. trinocular 8. An annular stop is used for which type of microscopy? A. confocal B. darkfield C. fluorescence D. phase contrast* 9. Which of the following is the specific name for a stain that colors the background but not the specimen? A. acid-fast stain B. counterstain C. differential stain D. negative stain* 10. Which type of microscopy would work best for viewing internal cell structures? A. atomic force microscopy B. scanning electron microscopy C. scanning tunneling microscopy D. transmission electron microscopy* 11. The Gram-staining procedure is best described as which of the following? A. complex staining B. differential staining* C. negative staining D. simple staining 12. When there is a substantial difference in refractive index between two materials, which of the following describes what will happen to light passing from one material to the other? A. It will fail to be refracted. B. It will undergo a large amount of refraction.* C. It will undergo a small amount of refraction. D. It will undergo a variable amount of refraction. 13. In microscopy, the focal length refers to which of the following? A. a description of the wavelength needed for an image to be in focus B. a measure of the amount of refraction produced by a lens C. a measure of the thickness of the lens needed for an image to be in focus D. the distance to the image point (at which all light entering a lens is parallel)* 14. Which of the following are pigments used in microscopy to absorb and reflect light? A. chromatographs B. chromophores* C. oilophores D. photophores 15. Negative staining is the standard approach used to visualize which structure(s)? A. capsules* B. endospores C. flagella D. nucleoid regions 16. Which is a standard mordant used in flagella staining? A. basic fuchsin B. iodine C. safranin D. tannic acid* 17. Which of the following pairs are common acid-fast staining techniques? A. Gram and Kinyoun B. negative and Schaeffer-Fulton C. Ziehl-Neelsen and Kinyoun* D. Ziehl-Neelsen and Schaeffer-Fulton 18. Which is the primary stain used in the Ziehl-Neelsen technique? A. acid-alcohol B. carbolfuchsin* C. crystal violet D. methylene blue 19. Which is the correct order of steps in Gram staining? A. crystal violet stain, ethanol decolorization, Gram’s iodine mordant, safranin counterstain B. crystal violet stain, Gram’s iodine mordant, ethanol decolorization, safranin counterstain* C. ethanol stain, crystal violet rinse, safranin counterstain, Gram’s iodine mordant D. safranin stain, Gram’s iodine mordant, ethanol decolorization, crystal violet counterstain 20. It is important to fix bacterial smears on a slide for which of the following reasons? A. to attach them to the slide* B. to cause swelling of the cell to make interior structures more visible C. to enhance the uptake of stains 21. Which of the following is not commonly used for chemical fixation? A. acetic acid B. ethanol C. glutaraldehyde D. iodine* 22. Which of the following is not involved in preparing a bacterial slide for Gram staining? A. allowing the sample to dry on the slide B. fixing the specimen to the slide C. placing a smear on the slide D. preparing a wet mount* 23. Which of the following most specifically refers to stains with positively charged chromophores? A. acid-fast dyes B. acidic dyes C. basic dyes* D. positive dyes 24. Which of the following most specifically refers to a stain that dyes a specimen rather than the background? A. counterstain
Written for
- Institution
- OpenStax Microbiology
- Course
- OpenStax Microbiology
Document information
- Uploaded on
- April 8, 2024
- Number of pages
- 17
- Written in
- 2023/2024
- Type
- Exam (elaborations)
- Contains
- Questions & answers
Subjects
-
openstax microbiology test bank chapter 2 how we
Also available in package deal