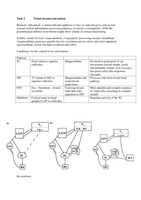
Perception
The visual system
The eye
- When you see something, light is reflected off
something. This is altered by the lens and projected on
the retina.
- Fovea -> the point where you see sharpest.
- Blind spot -> when you look directly at something.
This is because there are no cones and rods because all
the fibers leave the eye at this point, thus, there are no
photoreceptors. However, your brain fills up this
place. Thus, we are not aware of this blind spot.
- Optic chiasm -> where information of the two eyes
crosses.
- Visual information -> dorsal route is ‘where’, ventral route is ‘what’.
Impairment
- Hemianopia -> see image below.
- Neglect -> deficit in attention. It is difficult to distinguish from hemianopias (lesion location).
o Hemianopia -> patients are often aware that they miss a part of their visual field. If
there is clear damage in the visual cortex, it is probably related to this.
o Neglect -> patients are not aware of their defect. Patients are biased to one side and
they have mixed eye movements that are mainly focused on one part in space.
Mainly the right temporal lobe is damaged, but this is not always the case.
- Akinetopsia -> there is a deficit in motion perception. There is bilateral damage in V5/MT.
- Prosopagnosia -> deficit in face perception. They can see faces, but can not recognize it.
There is damage in the fusiform face area.
- Visual agnosia -> impaired visual recognition of objects. There is no deficit in vision,
language, memory etc.
1