EXAM 2 REVIEW: BIOLOGIC MODULE
Neurons:
- Cells within our nervous system
- Communicates info & handles info processing
- Reason why neurons are base for psychology and human mind
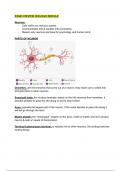
PARTS OF NEURON
Dendrites: are the branches that come out of a neuron; they reach out to collect info
and give them to other neurons
Soma/cell body: the nucleus basically, based on the info received from dendrites, it
decides whether to pass the info along or just to stop it there
Axon: typically the largest part of the neuron; if the soma decides to pass info along it
will def go through the axon
Myelin sheath: the “rectangular” shapes on the axon, made of myelin and its to protect
neuron & help w/ speed of transmission
Terminal buttons/axon terminal: to release info to other neurons, the ending branches
looking things
, Synapse: space between two neurons, healthy neurons should NOT be touching, and
its a problem in your nervous system if its touching.
*dendrite of one neuron > terminal button of another neuron
Glial cells - NOT NEURONS, but help neurons
- Support neuronal communication:
- Help neurons to have easier communication
- Amplifies what a neuron is saying to another neuron/blocking out
irrelevant info from other neurons
- Skeletal system: to help neurons to be where its suppose to be
- Nourishment: helps get nourishment (glucose in blood) for neurons so they
function
- Myelin: helps create myelin
- Repairs damage:
- In body: repair neurons to its traditional functioning (takes a long time
though)
- Brain damage: instead of repairing (b/c it snearly impossible) it will
facilitate other neurons to take over functions instead
- Remove waste from nourishment
- Helps create blood brain barrier, this barrier shields the brain from toxic
substances in the blood (poison), supplies brain tissues with nutrients, and filters
harmful compounds from the brain back to the bloodstream
Types of neurons
- Sensory: connected to different sense organs, how our senses give info to our
brain, a lot of our neurons are sensory neurons
- Motor: connected to our muscle and skeletal system, how our brain tells our
bodies to move
- Sensory = Afferent (moving info to the brain), Motor = Efferent (moving info
away from the brain)
Neurons:
- Cells within our nervous system
- Communicates info & handles info processing
- Reason why neurons are base for psychology and human mind
PARTS OF NEURON
Dendrites: are the branches that come out of a neuron; they reach out to collect info
and give them to other neurons
Soma/cell body: the nucleus basically, based on the info received from dendrites, it
decides whether to pass the info along or just to stop it there
Axon: typically the largest part of the neuron; if the soma decides to pass info along it
will def go through the axon
Myelin sheath: the “rectangular” shapes on the axon, made of myelin and its to protect
neuron & help w/ speed of transmission
Terminal buttons/axon terminal: to release info to other neurons, the ending branches
looking things
, Synapse: space between two neurons, healthy neurons should NOT be touching, and
its a problem in your nervous system if its touching.
*dendrite of one neuron > terminal button of another neuron
Glial cells - NOT NEURONS, but help neurons
- Support neuronal communication:
- Help neurons to have easier communication
- Amplifies what a neuron is saying to another neuron/blocking out
irrelevant info from other neurons
- Skeletal system: to help neurons to be where its suppose to be
- Nourishment: helps get nourishment (glucose in blood) for neurons so they
function
- Myelin: helps create myelin
- Repairs damage:
- In body: repair neurons to its traditional functioning (takes a long time
though)
- Brain damage: instead of repairing (b/c it snearly impossible) it will
facilitate other neurons to take over functions instead
- Remove waste from nourishment
- Helps create blood brain barrier, this barrier shields the brain from toxic
substances in the blood (poison), supplies brain tissues with nutrients, and filters
harmful compounds from the brain back to the bloodstream
Types of neurons
- Sensory: connected to different sense organs, how our senses give info to our
brain, a lot of our neurons are sensory neurons
- Motor: connected to our muscle and skeletal system, how our brain tells our
bodies to move
- Sensory = Afferent (moving info to the brain), Motor = Efferent (moving info
away from the brain)