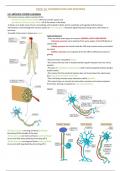
Psychodynamic Approaches 3
Part 1
Jungian psychotherapy
Jung’s therapy can be described as the process of individuation
His views on mental disorders were fairly inconsistent with the medical model
o “Clinical diagnoses are important… but they do not help the patient. The
crucial thing is the story. For it alone shows the human background and the
human suffering, and only at that point can the doctors therapy begin to
operate” . “in therapy the problem is always the whole person and never the
symptom alone, we have to ask questions which challenge the whole
personality”. – Carl Jung
o ^^used psychological formulation early on in 20th century
o He never really clearly identified the specific factors that contribute to the
lower levels of individuation and there were many different factors as part of
his views on human psyche that he felt could contribute to people
experiencing mental distress such as an imbalance between consciousness
and unconsciousness (rigid personas, personality complexes, clashes
between attitude and function types)
o Mental disorders could be due to extremities in attitudes or functions, in
accordance to Jung’s thoughts and definitions:
Hysteria – defined as extreme extraversion, comes out as a neurotic
disorder, libido is concerned with moving away from inner integrity
and is concerned with social relationships in outside world (persona)
Schizophrenia defined as extreme introversion, comes out as a
psychotic disorder, the libido argued to withdraw from reality, go into
own fantasy of their own thoughts and beliefs because of that
conscious is much more influential hence delusions and
hallucinations.
His views on neuroses
o Mental health disorder – imbalance between needs of the individual in terms
of their own individuation and needs of the collective
o Neuroses – homeostatic imbalance between conscious and unconscious. Jung
argued neuroses arise due to an imbalance between unconscious and
conscious
o Symptom formation is part of the individuation process
o Freud argued neuroses developed in early childhood whereas Jung believed it
could develop in any stage of the lifecyle. Freud believed it to be a more
backward looking reductive process whereas Jung believed it to be more
forward looking
o Underdeveloped individuality and atrophied collective adaptation
, o Saw neuroses as an escape from a challenging life even that the individual
feels unequipped to deal with. Suffering of a soul that has not yet found
meaning.
Jung’s analytical therapy
o Analysis tailored to the individual and depends on their stage of life,
personality characteristics, nature of their problems.
o Aims
Attain goals, deal with complexes, strengthen consciousness
Achieve homeostatic balance
Understand the inner self (for most) (for middle aged as they want to
truly understand inner self and identify ones meaning in life)
Achieve self-actualisation (for some) (for the youth as they go off to
attain life goals)
Most of Jung’s clients were in second half of life and about one third
had no discernible clinical condition rather felt life was aimless and
meaningless. For these the goal was to self-actualise involving a
deeper comprehension of their psyche and finding a new balance
between conscious and unconscious.
o Therapy procedure – less intense than Freud
2-3 sessions per week, break after 10 weeks
Analysis as an eye-to-eye dialogue – client allowed to discuss with
therapist, forming a dialogue between the two.
Therapist can be human, confrontational if necessary
Four stages to therapy
o 1) confession – individual uses cathartic confession to bring inhibited
emotions or thoughts to light when they’re not usually part of an individual’s
consciousness
o 2) Elucidation – interpretation of projects e.g. dreams
o 3) Education – learn new adaptive habits to attain goals and realise potential
self-actualisation
o 4) Transformation – not everyone needs it. Those looking for individuation do
and go through self-acceptance.
Therapeutic interventions – 3 of them
o Analysis of transference
Understanding projected unconscious content
Deal with personal and collective unconscious projections – negative
projections (part of a shadow) possibly thoughts and beliefs the
clients wish to change, positive projections coming to the realisation
and acceptance that they are at that stage and want to develop.
By making thoughts more apparent into consciousness gives client
more psychic energy – can focus on goals that they have
Learn to discriminate between personal and impersonal contents that
are projected e.g. se therapist as an archetypal person.
Transference is completed when client objectifies impersonal content.
Essential part of process of individuation. Need to assume
responsibility and no longer place guarantees of happiness based on
factors outside of the self.
Part 1
Jungian psychotherapy
Jung’s therapy can be described as the process of individuation
His views on mental disorders were fairly inconsistent with the medical model
o “Clinical diagnoses are important… but they do not help the patient. The
crucial thing is the story. For it alone shows the human background and the
human suffering, and only at that point can the doctors therapy begin to
operate” . “in therapy the problem is always the whole person and never the
symptom alone, we have to ask questions which challenge the whole
personality”. – Carl Jung
o ^^used psychological formulation early on in 20th century
o He never really clearly identified the specific factors that contribute to the
lower levels of individuation and there were many different factors as part of
his views on human psyche that he felt could contribute to people
experiencing mental distress such as an imbalance between consciousness
and unconsciousness (rigid personas, personality complexes, clashes
between attitude and function types)
o Mental disorders could be due to extremities in attitudes or functions, in
accordance to Jung’s thoughts and definitions:
Hysteria – defined as extreme extraversion, comes out as a neurotic
disorder, libido is concerned with moving away from inner integrity
and is concerned with social relationships in outside world (persona)
Schizophrenia defined as extreme introversion, comes out as a
psychotic disorder, the libido argued to withdraw from reality, go into
own fantasy of their own thoughts and beliefs because of that
conscious is much more influential hence delusions and
hallucinations.
His views on neuroses
o Mental health disorder – imbalance between needs of the individual in terms
of their own individuation and needs of the collective
o Neuroses – homeostatic imbalance between conscious and unconscious. Jung
argued neuroses arise due to an imbalance between unconscious and
conscious
o Symptom formation is part of the individuation process
o Freud argued neuroses developed in early childhood whereas Jung believed it
could develop in any stage of the lifecyle. Freud believed it to be a more
backward looking reductive process whereas Jung believed it to be more
forward looking
o Underdeveloped individuality and atrophied collective adaptation
, o Saw neuroses as an escape from a challenging life even that the individual
feels unequipped to deal with. Suffering of a soul that has not yet found
meaning.
Jung’s analytical therapy
o Analysis tailored to the individual and depends on their stage of life,
personality characteristics, nature of their problems.
o Aims
Attain goals, deal with complexes, strengthen consciousness
Achieve homeostatic balance
Understand the inner self (for most) (for middle aged as they want to
truly understand inner self and identify ones meaning in life)
Achieve self-actualisation (for some) (for the youth as they go off to
attain life goals)
Most of Jung’s clients were in second half of life and about one third
had no discernible clinical condition rather felt life was aimless and
meaningless. For these the goal was to self-actualise involving a
deeper comprehension of their psyche and finding a new balance
between conscious and unconscious.
o Therapy procedure – less intense than Freud
2-3 sessions per week, break after 10 weeks
Analysis as an eye-to-eye dialogue – client allowed to discuss with
therapist, forming a dialogue between the two.
Therapist can be human, confrontational if necessary
Four stages to therapy
o 1) confession – individual uses cathartic confession to bring inhibited
emotions or thoughts to light when they’re not usually part of an individual’s
consciousness
o 2) Elucidation – interpretation of projects e.g. dreams
o 3) Education – learn new adaptive habits to attain goals and realise potential
self-actualisation
o 4) Transformation – not everyone needs it. Those looking for individuation do
and go through self-acceptance.
Therapeutic interventions – 3 of them
o Analysis of transference
Understanding projected unconscious content
Deal with personal and collective unconscious projections – negative
projections (part of a shadow) possibly thoughts and beliefs the
clients wish to change, positive projections coming to the realisation
and acceptance that they are at that stage and want to develop.
By making thoughts more apparent into consciousness gives client
more psychic energy – can focus on goals that they have
Learn to discriminate between personal and impersonal contents that
are projected e.g. se therapist as an archetypal person.
Transference is completed when client objectifies impersonal content.
Essential part of process of individuation. Need to assume
responsibility and no longer place guarantees of happiness based on
factors outside of the self.