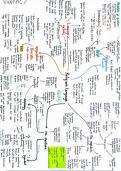
scalars magnitude
magnitude and
Vectors
direction
Resolution addition of vectors
Scalars and Vectors
Definition
Scalars are those quantities that have only magnitude and no direction while
Vectors are those quantities that have both magnitude and direction
Difference between scalar and vector
scalar vector
It has only magnitude It has magnitude and direction
It can be described with only magnitude It cannot be described with only
magnitude
It is resolved with ordinary algebraic It is resolved with geometrical methods
, methods
Vector Representation
A vector is represented by a straight line where;
The length of the line (L) = magnitude of the vector
Arrow head (A) = direction of the vector
Vector Addition
When 2 vectors act on a point, the angle between them determines the method
used to find the sum. The sum of the vectors is also called the Resultant of the 2
vectors.
Resultant vector is a single vector that has the same effect in magnitude and
direction as the original vector acting together.
A. If the angle between them is 0 or 360 degrees (same direction)
The resultant vector (R) is the sum of vector A and B
R=A+B
magnitude and
Vectors
direction
Resolution addition of vectors
Scalars and Vectors
Definition
Scalars are those quantities that have only magnitude and no direction while
Vectors are those quantities that have both magnitude and direction
Difference between scalar and vector
scalar vector
It has only magnitude It has magnitude and direction
It can be described with only magnitude It cannot be described with only
magnitude
It is resolved with ordinary algebraic It is resolved with geometrical methods
, methods
Vector Representation
A vector is represented by a straight line where;
The length of the line (L) = magnitude of the vector
Arrow head (A) = direction of the vector
Vector Addition
When 2 vectors act on a point, the angle between them determines the method
used to find the sum. The sum of the vectors is also called the Resultant of the 2
vectors.
Resultant vector is a single vector that has the same effect in magnitude and
direction as the original vector acting together.
A. If the angle between them is 0 or 360 degrees (same direction)
The resultant vector (R) is the sum of vector A and B
R=A+B