Lecture 1: Evolutionary problem solving
Kickoff
● Evolution can create intelligence
● Artificial evolution can create artificial intelligence
● Generic system architecture: Triangle of Life
What is Evolutionary Computing (EC)?
● The field for designing, applying, and studying evolutionary algorithms
● What is an evolutionary algorithm?
● What is evolution?
● What is an algorithm?
○ Set of steps to accomplish a task
○ What makes it good: correctness and efficiency
○ Asymptotic analysis: computing the running time of any operation in
mathematical units of computation
■ To determine which algorithm is more efficient
Evolutionary heuristic example: 8 queens problem
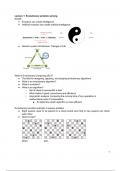
● Eight queens need to be placed on a chess board such that no two queens can check
each other
● Good or bad?
Good bad
1
,General (implicit) vs. specific (explicit)
● General: N > 1 queens
● Specific: N = 8
● The property “size” is sufficiently specific
● Problem ≠ problem instance
8 queens solver
● Method 1
○ Place queens one by one
○ Fill rows from top to bottom, within a row: first available from left to right
○ Backtrack if stuck
■ Works by extending an empty solution – constructive method
■ Recursive
■ Blind
■ Search trajectory via correct but incomplete configurations
● Method 2 (is the same as method 1), but
○ Within a row: choose position that checks the least number of other positions
○ scan from left to right
2
, ■ Works by extending an empty solution – constructive method
■ Recursive
■ Heuristic: try to minimize need for backtracks
■ Search trajectory via correct but incomplete configurations
● Method 1 vs. Method 2
First possible Minimize “checks”
● Method 3
○ Place all queens
○ Repair errors by
■ Choose queen with the most conflicts
■ Move it to the best position in the same row
○ “best position”= with the min. number of conflicts
○ Random move if stuck
■ Works by improving a solution – iterative improvement method
■ Heuristic: try to maximize improvement via “educated guess”
■ Search trajectory via complete but incorrect configurations
● Method 4
○ Place all queens
○ Improve configuration by
■ Make K > 1 new configurations by a few random changes (“mutations”)
■ Discard the worst K-1 “mutants” (thus keep the best only)
○ Iterate
■ Works by improving a solution – iterative improvement method
3
Kickoff
● Evolution can create intelligence
● Artificial evolution can create artificial intelligence
● Generic system architecture: Triangle of Life
What is Evolutionary Computing (EC)?
● The field for designing, applying, and studying evolutionary algorithms
● What is an evolutionary algorithm?
● What is evolution?
● What is an algorithm?
○ Set of steps to accomplish a task
○ What makes it good: correctness and efficiency
○ Asymptotic analysis: computing the running time of any operation in
mathematical units of computation
■ To determine which algorithm is more efficient
Evolutionary heuristic example: 8 queens problem
● Eight queens need to be placed on a chess board such that no two queens can check
each other
● Good or bad?
Good bad
1
,General (implicit) vs. specific (explicit)
● General: N > 1 queens
● Specific: N = 8
● The property “size” is sufficiently specific
● Problem ≠ problem instance
8 queens solver
● Method 1
○ Place queens one by one
○ Fill rows from top to bottom, within a row: first available from left to right
○ Backtrack if stuck
■ Works by extending an empty solution – constructive method
■ Recursive
■ Blind
■ Search trajectory via correct but incomplete configurations
● Method 2 (is the same as method 1), but
○ Within a row: choose position that checks the least number of other positions
○ scan from left to right
2
, ■ Works by extending an empty solution – constructive method
■ Recursive
■ Heuristic: try to minimize need for backtracks
■ Search trajectory via correct but incomplete configurations
● Method 1 vs. Method 2
First possible Minimize “checks”
● Method 3
○ Place all queens
○ Repair errors by
■ Choose queen with the most conflicts
■ Move it to the best position in the same row
○ “best position”= with the min. number of conflicts
○ Random move if stuck
■ Works by improving a solution – iterative improvement method
■ Heuristic: try to maximize improvement via “educated guess”
■ Search trajectory via complete but incorrect configurations
● Method 4
○ Place all queens
○ Improve configuration by
■ Make K > 1 new configurations by a few random changes (“mutations”)
■ Discard the worst K-1 “mutants” (thus keep the best only)
○ Iterate
■ Works by improving a solution – iterative improvement method
3