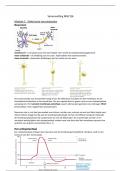
Week 1: Chapter 14 (14.1 – 14.3) Which of the following is ionizing radiation?
True or False. Exothermic reactions are always faster than endothermic reactions? False alpha particles, beta particles, X-rays, gamma radiation
The units for a rate constant, k, are: dependent upon the overall order of the reaction. Week 3: Chapter 15
Which of the following statements correctly describes a system at equilibrium?
For the following gaseous reaction in a sealed vessel the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
2 C8H11 (l) + 25 O2 (g) → 18 H2O (g) + 16 CO2 (g)
the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (products) was The reaction of carbon disulfide with hydrogen gas will produce methane gas and
measured at two time points and these data were hydrogen sulfide gas as follows: CS2 (g) + 4 H2 (g) ⇌ CH4 (g) + 2 H2S (g) Initially, a
obtained.
mixture of 0.850 atm CS2 and 1.50 atm H2 were placed in the reaction chamber
Time PCO2
together. What is the partial pressure for CH4 once the reaction reaches equilibrium
0s 150 torr
hint: Kp = 3.0 x 10-6 at 900C
20 s 650 torr
Use ICE table to solve. 0.0148 atm.
From this information, calculate the rate of oxygen
consumption over the same time period. 39 torr/s
At 100C the value of the equilibrium constant, Kc = 2.5 x 10-6 for the following
The following reaction: A + 2B → C is found to have the rate law: rate = k [A] [B]2. If [A] reaction. 2 Cr (s) + 3 Br2 (g) 2 CrBr3 (s) If the reaction temperature is increased t
is tripled and [B] is doubled, by what factor does the reaction rate change? 750C and allowed to again reach equilibrium, the value of the equilibrium constant
k = 1, rate = [A][B]2 rate = (1)(2)2 rate = (3)(2)2 = 12 increases to Kc = 5.0 x 10-2. What does this indicate about the reaction?
Rate increases by a factor 12. the reaction is endothermic.
Given the hypothetic reaction: 2 A (g) + 2 B (g) → 4 C (g) + D (g) From the following data,
deduce the rate law for the reaction. rate = k[A]m [B]n At 823C, Kp = 490 for the equilibrium reaction, CoO (s) + CO (g) Co (s) + CO2
Experiment [A] (M) [B] (M) Initial Rate (M • min-1) (g) What is the value of Kc at the same temperature for the equilibrium below?
1 0.5 x 10-7 0.122 0.00602 Co (s) + CO2 (g) CoO (s) + CO (g) (hint: Kp = Kc(RT)∆n, R = 0.08206
2 1.0 x 10-7 0.244 0.0482 L•atm/mol•K
3 0.5 x 10-7 0.488 0.0963 Kp’ = 1/Kp = 1/490 = 2.04 x 10-3 823 + 273 = 1096 K
Kc = Kp / (RT)∆n = 2.04 x 10-3 / (0.08206 x 1096) (1) = 2.04 x 10-3
4 2.0 x 10-7 0.488 0.385
2.04 x 10-3
to find m: (2.0 x 10-7/0.5 x 10-7) = 0.385/0.0963 = 4m = 4, so m = 1
to find n: (0.488/0.122)n = 0.0963/0.00602 = 4n = 16, so n = 2
rate = k [A][B]2 H2, I2, and HI are introduced in a flask. H2 (g) + I2 (g) ⇌ 2HI (g) Kc = 54.2
If the initial concentrations of H2 and I2 are both 0.16 M and their equilibrium
Concerning the decomposition of A, A → products, which of the following methods concentrations are both 0.072 M, what was the initial concentration of HI?
could be used to determine the order of the reaction with respect to A? Use ICE table to solve. 0.35 M
I. Plot [A] vs time, ln[A] vs time, and 1/[A[ vs tine and identify which plot yields a straight
line. Which of the following will change the value of an equilibrium constant?
II. Vary the concentration of A and note by what factor the rate changes. changing the reaction temperature.
III. Identify if successive half-lives of A double, half, or stay constant.
I, II, and III Considering the reaction: SO2Cl2 (g) ⇌ SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g) where Kc = 0.078 at 100C
Suppose 0.500 moles of SO2Cl2, 0.035 moles of SO2, and 0.080 moles of Cl2 are
A reaction was experimentally determined to follow the rate law, Rate = k[A] 2, where k =
0.456 s-1M-1. Starting with [A]0 = 0.500 M, how many seconds will it take for [A]t = 0.250 combined in an evacuated 5.00 L flask and heated to 100C. Which statement best
M? describes these reaction conditions?
kt = 1/[A]t – 1/[A]0, rearrange to find t Q<K and the reaction will go in the forward direction.
t = (1/0.250 M) – (1/0.500 M) / 0.456 s-1M-1
4.39 s Solid NH4SH is introduced into an evacuated flask at 24C. The following reaction
takes place: NH4SH (s) NH3 (g) + H2S (g) At equilibrium, the total pressure, P T,
The half-life of a first order reaction is 13 minutes. If the initial concentration of the equal to the sum of the partial pressures, P T = PNH3 + PH2S, is 0.614 atm. What is the
reactant is 0.085 M, how long (in min) will it take for the concentration to decrease to value of the equilibrium constant Kp at 24C?
0.0106 M? Use ICE table to solve. 0.0943
t ½ = 0.693 / k, rearrange to find k, k = 0.693 / t ½ = 0. min
k = 0.0533 min-1, use ln ([A]t / [A]0) = -tk, solve for t
One of the environmentally important reactions involved in acid rain production has
ln (0.0106 M / 0.085 M) = -(0.0533 min-1)t
t = 39 min the following expression for the equilibrium constant, K: K = [SO 3] / [SO] [O2]1/2 Fro
the expression, what would be the balanced chemical reaction?
Week 2: Chapter 14 (14.4 – 14.6) & Chapter 21 SO2 (g) + 1/2O2 (g) SO3 (g)
An increase in the temperature of the reactants causes an increase in the rate of reaction. The
best explanation for this behavior is that as the temperature increases, ______________. Given the Kc value for the following reaction at a particular temperature: 2 NO (g) +
the fraction of collisions with total kinetic energy great than Ea increases. Br2 (g) ⇌ 2 NOBr (g) Kc = 0.013. What is the value of Kc for the new equilibrium
below at the same temperature? NOBr (g) ⇌ NO (g) + 1/2Br2 (g)
NO2 (g) + CO2 (g) → NO3 (g) + CO (g) reversed Kc’ = 1/Kc = 1/0.013 = 76.9
For this reaction, the molecularity is _______, and the rate law is ______. x ½ Kc” = (Kc1)1/2 = (76.9)1/2 = 76.9 = 8.8
bimolecular, rate = k[NO2][CO2]
The following reaction has a Kc value of 2.0 x 10-4 at 723 K: 2 HI (g) ⇌ H2 (g) + I2 (
How many protons and neutrons are in the following nucleus? 108Ag
Which of the following statements best describes the composition of the reaction
47 protons and 62 neutrons
mixture at equilibrium?
It has been suggested by some that strontium-90 (generated by nuclear testing) deposited in there are more reactants than products; reactants predominate.
the hot Arizona desert will undergo radioactive decay more rapidly because it will be
exposed to much higher than average temperatures. Is this a reasonable suggestion? Consider the following chemical reaction at a specific temperature: H2 (g) + I2 (g) ⇌
no HI (g) Kc = 35 At equilibrium in a particular experiment, the concentrations of H 2 an
I2 were 0.25 M and 0.035 M, respectively. What is the equilibrium concentration of
41Cadecays by electron capture. The product of this nuclear reaction undergoes alpha decay. HI (in M) for this reaction?
What is the resulting element? Cl 35 = [HI]2 / (0.25)(0.035) [HI] = 0.55 M
Cesium-131 has a half-life of 9.7 days. What percent (in %) of a cesium-131 sample would At 80C, Kp = 840 for the following reaction: PH3BCl3 (s) ⇌ PH3 (g) + BCl3 (g) A
remain after 60 days? 1.4 sample of solid PH3BCl3 is placed in a closed 1.0 L vessel and allowed to decompose
k = 0.693/9.7 = 0.0714 until it reaches equilibrium. What is the partial pressure of PH3 (in atm) at
ln (Nt/N0) = - (0.0714 day-1)(60 day) = -4.2866
equilibrium?
= e-4.2866 = 0.0138 x 100 = 1.4%
Use ICE table to solve.
The mass of a proton is 1.673 x 10-24 g. The mass of a neutron is 1.675 x 10-24 g. The mass of Kp = PPH3 • PBCl3
the nucleus of a 56Fe atom is 9.289 x 10-23 g. What is the nuclear binding energy (in J) for a 840 = (x)(x) = x2 x = 840 = 29 atm
56Fe nucleus? hint: the speed of light © is 3.00 x 10 8 m/s.
DE = DmC2 Dm = mass of nucleus – S mass (p + n) For the reaction: PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g) ⇌ PCl5 (g) ∆H = -87.9 kJ
26 iron protons, 56-26 = 30 neutrons Which change will shift the position of the equilibrium to the left?
9.289 x 10-23 – [26 (1.673 x 10-24] + 30 (1.675 x 10-24) = -8.58 x 10-25 g Increase volume.
Convert to KG for E=Mc2 formula, -8.58 x 10-28 KG
E = (-8.58 x 10-28) (3.00 x 108)2 E = 7.72 x 10-11
True or False. Exothermic reactions are always faster than endothermic reactions? False alpha particles, beta particles, X-rays, gamma radiation
The units for a rate constant, k, are: dependent upon the overall order of the reaction. Week 3: Chapter 15
Which of the following statements correctly describes a system at equilibrium?
For the following gaseous reaction in a sealed vessel the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction.
2 C8H11 (l) + 25 O2 (g) → 18 H2O (g) + 16 CO2 (g)
the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (products) was The reaction of carbon disulfide with hydrogen gas will produce methane gas and
measured at two time points and these data were hydrogen sulfide gas as follows: CS2 (g) + 4 H2 (g) ⇌ CH4 (g) + 2 H2S (g) Initially, a
obtained.
mixture of 0.850 atm CS2 and 1.50 atm H2 were placed in the reaction chamber
Time PCO2
together. What is the partial pressure for CH4 once the reaction reaches equilibrium
0s 150 torr
hint: Kp = 3.0 x 10-6 at 900C
20 s 650 torr
Use ICE table to solve. 0.0148 atm.
From this information, calculate the rate of oxygen
consumption over the same time period. 39 torr/s
At 100C the value of the equilibrium constant, Kc = 2.5 x 10-6 for the following
The following reaction: A + 2B → C is found to have the rate law: rate = k [A] [B]2. If [A] reaction. 2 Cr (s) + 3 Br2 (g) 2 CrBr3 (s) If the reaction temperature is increased t
is tripled and [B] is doubled, by what factor does the reaction rate change? 750C and allowed to again reach equilibrium, the value of the equilibrium constant
k = 1, rate = [A][B]2 rate = (1)(2)2 rate = (3)(2)2 = 12 increases to Kc = 5.0 x 10-2. What does this indicate about the reaction?
Rate increases by a factor 12. the reaction is endothermic.
Given the hypothetic reaction: 2 A (g) + 2 B (g) → 4 C (g) + D (g) From the following data,
deduce the rate law for the reaction. rate = k[A]m [B]n At 823C, Kp = 490 for the equilibrium reaction, CoO (s) + CO (g) Co (s) + CO2
Experiment [A] (M) [B] (M) Initial Rate (M • min-1) (g) What is the value of Kc at the same temperature for the equilibrium below?
1 0.5 x 10-7 0.122 0.00602 Co (s) + CO2 (g) CoO (s) + CO (g) (hint: Kp = Kc(RT)∆n, R = 0.08206
2 1.0 x 10-7 0.244 0.0482 L•atm/mol•K
3 0.5 x 10-7 0.488 0.0963 Kp’ = 1/Kp = 1/490 = 2.04 x 10-3 823 + 273 = 1096 K
Kc = Kp / (RT)∆n = 2.04 x 10-3 / (0.08206 x 1096) (1) = 2.04 x 10-3
4 2.0 x 10-7 0.488 0.385
2.04 x 10-3
to find m: (2.0 x 10-7/0.5 x 10-7) = 0.385/0.0963 = 4m = 4, so m = 1
to find n: (0.488/0.122)n = 0.0963/0.00602 = 4n = 16, so n = 2
rate = k [A][B]2 H2, I2, and HI are introduced in a flask. H2 (g) + I2 (g) ⇌ 2HI (g) Kc = 54.2
If the initial concentrations of H2 and I2 are both 0.16 M and their equilibrium
Concerning the decomposition of A, A → products, which of the following methods concentrations are both 0.072 M, what was the initial concentration of HI?
could be used to determine the order of the reaction with respect to A? Use ICE table to solve. 0.35 M
I. Plot [A] vs time, ln[A] vs time, and 1/[A[ vs tine and identify which plot yields a straight
line. Which of the following will change the value of an equilibrium constant?
II. Vary the concentration of A and note by what factor the rate changes. changing the reaction temperature.
III. Identify if successive half-lives of A double, half, or stay constant.
I, II, and III Considering the reaction: SO2Cl2 (g) ⇌ SO2 (g) + Cl2 (g) where Kc = 0.078 at 100C
Suppose 0.500 moles of SO2Cl2, 0.035 moles of SO2, and 0.080 moles of Cl2 are
A reaction was experimentally determined to follow the rate law, Rate = k[A] 2, where k =
0.456 s-1M-1. Starting with [A]0 = 0.500 M, how many seconds will it take for [A]t = 0.250 combined in an evacuated 5.00 L flask and heated to 100C. Which statement best
M? describes these reaction conditions?
kt = 1/[A]t – 1/[A]0, rearrange to find t Q<K and the reaction will go in the forward direction.
t = (1/0.250 M) – (1/0.500 M) / 0.456 s-1M-1
4.39 s Solid NH4SH is introduced into an evacuated flask at 24C. The following reaction
takes place: NH4SH (s) NH3 (g) + H2S (g) At equilibrium, the total pressure, P T,
The half-life of a first order reaction is 13 minutes. If the initial concentration of the equal to the sum of the partial pressures, P T = PNH3 + PH2S, is 0.614 atm. What is the
reactant is 0.085 M, how long (in min) will it take for the concentration to decrease to value of the equilibrium constant Kp at 24C?
0.0106 M? Use ICE table to solve. 0.0943
t ½ = 0.693 / k, rearrange to find k, k = 0.693 / t ½ = 0. min
k = 0.0533 min-1, use ln ([A]t / [A]0) = -tk, solve for t
One of the environmentally important reactions involved in acid rain production has
ln (0.0106 M / 0.085 M) = -(0.0533 min-1)t
t = 39 min the following expression for the equilibrium constant, K: K = [SO 3] / [SO] [O2]1/2 Fro
the expression, what would be the balanced chemical reaction?
Week 2: Chapter 14 (14.4 – 14.6) & Chapter 21 SO2 (g) + 1/2O2 (g) SO3 (g)
An increase in the temperature of the reactants causes an increase in the rate of reaction. The
best explanation for this behavior is that as the temperature increases, ______________. Given the Kc value for the following reaction at a particular temperature: 2 NO (g) +
the fraction of collisions with total kinetic energy great than Ea increases. Br2 (g) ⇌ 2 NOBr (g) Kc = 0.013. What is the value of Kc for the new equilibrium
below at the same temperature? NOBr (g) ⇌ NO (g) + 1/2Br2 (g)
NO2 (g) + CO2 (g) → NO3 (g) + CO (g) reversed Kc’ = 1/Kc = 1/0.013 = 76.9
For this reaction, the molecularity is _______, and the rate law is ______. x ½ Kc” = (Kc1)1/2 = (76.9)1/2 = 76.9 = 8.8
bimolecular, rate = k[NO2][CO2]
The following reaction has a Kc value of 2.0 x 10-4 at 723 K: 2 HI (g) ⇌ H2 (g) + I2 (
How many protons and neutrons are in the following nucleus? 108Ag
Which of the following statements best describes the composition of the reaction
47 protons and 62 neutrons
mixture at equilibrium?
It has been suggested by some that strontium-90 (generated by nuclear testing) deposited in there are more reactants than products; reactants predominate.
the hot Arizona desert will undergo radioactive decay more rapidly because it will be
exposed to much higher than average temperatures. Is this a reasonable suggestion? Consider the following chemical reaction at a specific temperature: H2 (g) + I2 (g) ⇌
no HI (g) Kc = 35 At equilibrium in a particular experiment, the concentrations of H 2 an
I2 were 0.25 M and 0.035 M, respectively. What is the equilibrium concentration of
41Cadecays by electron capture. The product of this nuclear reaction undergoes alpha decay. HI (in M) for this reaction?
What is the resulting element? Cl 35 = [HI]2 / (0.25)(0.035) [HI] = 0.55 M
Cesium-131 has a half-life of 9.7 days. What percent (in %) of a cesium-131 sample would At 80C, Kp = 840 for the following reaction: PH3BCl3 (s) ⇌ PH3 (g) + BCl3 (g) A
remain after 60 days? 1.4 sample of solid PH3BCl3 is placed in a closed 1.0 L vessel and allowed to decompose
k = 0.693/9.7 = 0.0714 until it reaches equilibrium. What is the partial pressure of PH3 (in atm) at
ln (Nt/N0) = - (0.0714 day-1)(60 day) = -4.2866
equilibrium?
= e-4.2866 = 0.0138 x 100 = 1.4%
Use ICE table to solve.
The mass of a proton is 1.673 x 10-24 g. The mass of a neutron is 1.675 x 10-24 g. The mass of Kp = PPH3 • PBCl3
the nucleus of a 56Fe atom is 9.289 x 10-23 g. What is the nuclear binding energy (in J) for a 840 = (x)(x) = x2 x = 840 = 29 atm
56Fe nucleus? hint: the speed of light © is 3.00 x 10 8 m/s.
DE = DmC2 Dm = mass of nucleus – S mass (p + n) For the reaction: PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g) ⇌ PCl5 (g) ∆H = -87.9 kJ
26 iron protons, 56-26 = 30 neutrons Which change will shift the position of the equilibrium to the left?
9.289 x 10-23 – [26 (1.673 x 10-24] + 30 (1.675 x 10-24) = -8.58 x 10-25 g Increase volume.
Convert to KG for E=Mc2 formula, -8.58 x 10-28 KG
E = (-8.58 x 10-28) (3.00 x 108)2 E = 7.72 x 10-11