4. Signal transduction
1. Inductive signaling: cells talk to each other! ➔ important
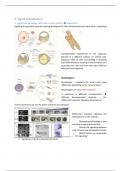
signaling is extremely important during development! Cells communicate with each other = signaling!
Transplantation experiment of the organizer
(dorsal) to a different embryo on ventral side.
Organizer talks to cells surrounding it changing
their differentiation resulting in the formation of a
secondary axis. (all cells have the same DNA but
different transcriptome).
Morphogens!!
Morphogen = substance for which cells react
differently depending on the concentration.
Morphogens are extremely important.
A substance in different concentrations ➔
different developmental response. = this
differential response regulates development.
In this experiment we see the works of Activin (morphogen).
Differential response regulates the
development of the embryo.
- Developmental biology is very
sensitive to signal transduction
- Disturb the signaling between
cells → learn how development works
- Which factors are responsible
for signaling?
Signaling is critical in developing foetus!
,2. Factors that cause signaling
Different factors are responsible for signaling:
- Physical forces → very important, different
depending on hard or soft tissue
- Cellular signaling cascades
- Cell behavior
Loop.
2.1. Physical forces → often forgotten!
Cell membranes with integrins (on outer side of membrane). The
cell membrane has a layer of integrins → transfer of force
- Extracellular membrane layer
- Integrins are also connected with intracellular actine-
signaling networks
- Cellular contraction
Experiment: Ab’s bind to outer side of cell
- Bead bound to Ab’s + cell in magnetic field
- Bead will bind to receptor outside cell and nucleus will
shrink
Everything is physically connected => nucleus knows what happens on outside of the cell. If something
happens on inside of cell → effect on outside of the cell.
Integrins connected to intracellular actin. Physical connection. Inside nucleus knows what’s going on
outside the cell.
Activation of YAP depends on environment: stiffness of ECM (extracellular matrix)
- When cells are dense/compact → TXN-factor in cytoplasm
(phosphorylated = inactive)
- Cells on soft ECM → TXN-factor in cytoplasm (phosphorylated =
inactive) → cells are compact on surface
- Cells on hard ECM → TXN-factor in nucleus (active) → cells will
stretch and spread over surface.
- YAP active: TXN-factor becomes active inside nucleus
- YAP inactive: TXN-factor stays in cytoplasm and is phosphorylated.
Regulation of phosphorylation YAP → hippo-pathway-signaling
➔Cells also listen to environment and not only
to molecules!
Stem cells will develop differently depending
on what they grow.
, Lower stiffness of substrate and higher density, TXN-factor will be inactive and in cytoplasm (look at
picture, previous page)
- Will happen in these situations: small surface, soft ECM, low tension of the cytoskeleton.
- This will lead to adipogenesis (formation of fat cells out of stem cells), growth stop and
apoptosis.
Higher stiffness of substrate and lower density: transcription factor will be active in nucleus.
- Will happen in these situations: large area and low density, on stiff and high cytoskeletal
tension.
- This will lead to proliferation and osteoblast differentiation.
➔Cells do not only listen to molecules, but also to substrate of ECM!!
Trophectoderm → TXN in cytoplasm
Inner cell mass, cells become compacter → TXN in nucleus
➔In absence of substance!
Physical interactions between cells, ectoderm
knows it’s ectoderm, etc.
Depending on how the YAS(niet YAP ?!) pathway
respons, cells know what to do, which subtype
to become.
Important: general scheme of signaling!!
Extracellular proteins + ligand (produced by a cell)
- Cell will express a receptor and protein/ligand will bind to it.
o No receptor = no response
o Receptor can be dimer, trimer, etc. but always the
same mechanism
- Different configurations of ligands and receptors
- Receptors signal that there is binding through second
messenger (often change in configuration of receptor).
o Passes signal from binding → phosphorylation
o Second messenger will go to nucleus → difference in expression of certain genes
- Something that binds on the outside of the cell → intracellular response → change in
expression of certain genes.
➔You can always fall back on this scheme.
Signaling pathways interact with each other! Signal cascades in the past signal networks now!
1. Inductive signaling: cells talk to each other! ➔ important
signaling is extremely important during development! Cells communicate with each other = signaling!
Transplantation experiment of the organizer
(dorsal) to a different embryo on ventral side.
Organizer talks to cells surrounding it changing
their differentiation resulting in the formation of a
secondary axis. (all cells have the same DNA but
different transcriptome).
Morphogens!!
Morphogen = substance for which cells react
differently depending on the concentration.
Morphogens are extremely important.
A substance in different concentrations ➔
different developmental response. = this
differential response regulates development.
In this experiment we see the works of Activin (morphogen).
Differential response regulates the
development of the embryo.
- Developmental biology is very
sensitive to signal transduction
- Disturb the signaling between
cells → learn how development works
- Which factors are responsible
for signaling?
Signaling is critical in developing foetus!
,2. Factors that cause signaling
Different factors are responsible for signaling:
- Physical forces → very important, different
depending on hard or soft tissue
- Cellular signaling cascades
- Cell behavior
Loop.
2.1. Physical forces → often forgotten!
Cell membranes with integrins (on outer side of membrane). The
cell membrane has a layer of integrins → transfer of force
- Extracellular membrane layer
- Integrins are also connected with intracellular actine-
signaling networks
- Cellular contraction
Experiment: Ab’s bind to outer side of cell
- Bead bound to Ab’s + cell in magnetic field
- Bead will bind to receptor outside cell and nucleus will
shrink
Everything is physically connected => nucleus knows what happens on outside of the cell. If something
happens on inside of cell → effect on outside of the cell.
Integrins connected to intracellular actin. Physical connection. Inside nucleus knows what’s going on
outside the cell.
Activation of YAP depends on environment: stiffness of ECM (extracellular matrix)
- When cells are dense/compact → TXN-factor in cytoplasm
(phosphorylated = inactive)
- Cells on soft ECM → TXN-factor in cytoplasm (phosphorylated =
inactive) → cells are compact on surface
- Cells on hard ECM → TXN-factor in nucleus (active) → cells will
stretch and spread over surface.
- YAP active: TXN-factor becomes active inside nucleus
- YAP inactive: TXN-factor stays in cytoplasm and is phosphorylated.
Regulation of phosphorylation YAP → hippo-pathway-signaling
➔Cells also listen to environment and not only
to molecules!
Stem cells will develop differently depending
on what they grow.
, Lower stiffness of substrate and higher density, TXN-factor will be inactive and in cytoplasm (look at
picture, previous page)
- Will happen in these situations: small surface, soft ECM, low tension of the cytoskeleton.
- This will lead to adipogenesis (formation of fat cells out of stem cells), growth stop and
apoptosis.
Higher stiffness of substrate and lower density: transcription factor will be active in nucleus.
- Will happen in these situations: large area and low density, on stiff and high cytoskeletal
tension.
- This will lead to proliferation and osteoblast differentiation.
➔Cells do not only listen to molecules, but also to substrate of ECM!!
Trophectoderm → TXN in cytoplasm
Inner cell mass, cells become compacter → TXN in nucleus
➔In absence of substance!
Physical interactions between cells, ectoderm
knows it’s ectoderm, etc.
Depending on how the YAS(niet YAP ?!) pathway
respons, cells know what to do, which subtype
to become.
Important: general scheme of signaling!!
Extracellular proteins + ligand (produced by a cell)
- Cell will express a receptor and protein/ligand will bind to it.
o No receptor = no response
o Receptor can be dimer, trimer, etc. but always the
same mechanism
- Different configurations of ligands and receptors
- Receptors signal that there is binding through second
messenger (often change in configuration of receptor).
o Passes signal from binding → phosphorylation
o Second messenger will go to nucleus → difference in expression of certain genes
- Something that binds on the outside of the cell → intracellular response → change in
expression of certain genes.
➔You can always fall back on this scheme.
Signaling pathways interact with each other! Signal cascades in the past signal networks now!