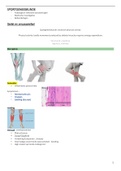
Negative Feedback – Body Temperature Negative Feedback – Body
Temperature
Body temperature increases above optimum
due to a change in environment or adrenaline.
The receptor that detects the change is the
hypothalamus.
The processing centre that coordinates the
response is the hypothalamus.
Sweat glands act as effectors & release beads
of sweat to cool down body temperature.
Body temperature decreases below optimum
due to a change in environment.
The receptor that detects the change is the
hypothalamus.
The processing centre that coordinates the
response is the hypothalamus.
Muscles act as effectors & act by shivering to
warm up body temperature.
Negative Feedback – Thyroxine Levels Negative Feedback – Thyroxine
Levels
Thyroxine levels increase above optimum.
The pituitary gland is the receptor that detects
the change.
The pituitary gland releases less/ no thyroid-
stimulating hormone (TSH)
The thyroid gland produces less/ no thyroxine.
Thyroxine levels decrease below optimum.
The pituitary gland is the receptor that detects
the change.
The pituitary gland releases thyrotropin
releasing hormone (TRH) which causes the
pituitary gland to release more TSH.
The thyroid gland releases more thyroxine.
Temperature
Body temperature increases above optimum
due to a change in environment or adrenaline.
The receptor that detects the change is the
hypothalamus.
The processing centre that coordinates the
response is the hypothalamus.
Sweat glands act as effectors & release beads
of sweat to cool down body temperature.
Body temperature decreases below optimum
due to a change in environment.
The receptor that detects the change is the
hypothalamus.
The processing centre that coordinates the
response is the hypothalamus.
Muscles act as effectors & act by shivering to
warm up body temperature.
Negative Feedback – Thyroxine Levels Negative Feedback – Thyroxine
Levels
Thyroxine levels increase above optimum.
The pituitary gland is the receptor that detects
the change.
The pituitary gland releases less/ no thyroid-
stimulating hormone (TSH)
The thyroid gland produces less/ no thyroxine.
Thyroxine levels decrease below optimum.
The pituitary gland is the receptor that detects
the change.
The pituitary gland releases thyrotropin
releasing hormone (TRH) which causes the
pituitary gland to release more TSH.
The thyroid gland releases more thyroxine.