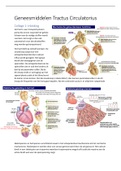
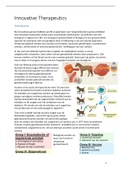
INVESTMENTS
EVALUSATING INVESTMENT OPTIONS:
1. Risk
- High investment = high returns/high loss.
- Diversification: all eggs not kept in one basket.
- Strategies to limit loss = Rebalancing: adjust your portfolio to get back
to the point where your portfolio diversifies.
2. Return on Investment (ROI)
- Measures efficiency of investment = what the investor will get back
over and above the original investment made.
3. Timeline
- Longer = greater risk can be taken e.g., if you’re 20 the you have years
to take risks.
4. Investment strategies
- Growth Strategy
Risk: high
Time: long-term
E.g.: shares
- Balanced Strategy
Risk: medium
Time: medium to long = aim is capital growth + some monthly
income.
E.g.: combination of equities = fixed deposit or rent income.
- Defensive strategy
Risk: low
Time: medium to long =aim on monthly income + some capital
growth.
E.g.: property, money in bank with smaller investment in equities.
- Conservative strategy
Risk: low to none
Time: any = aim on monthly income + maintaining capital invested.
E.g.: property ad cash instruments.
INVESTMENT OPTIONS:
EQUITY:
- Equity = shares
- Listed on JSE Ltd. = information on the shares’ performance available
for investors.
- If company is unlisted = company makes financial info available to
shareholders, banks, creditors, and SARS.
, - Options to become a shareholder are either from buying shares from
company issued the first time OR on the JSE from a previous
shareholder.
- Strategy to limit loss:
Stop-loss strategy: sell shares at predetermined price in order to stop
a loss – anything lower = deficit.
- Types of shares:
Ordinary shares:
o Holders have voting power.
o Holders’ returns come from APPRECIATION in the market value
of the shares and receiving company DIVIDENDS.
o Holders face higher risks.
Preference shares:
o Holders have NO voting power.
o Holders receive dividends BEFORE ordinary shareholders.
o Holders can claim the company’s assets BEFORE ordinary
shareholders if the companies go into liquidations.
- Risk:
High to moderate.
JSE: strict rules to protect investors and to decrease the risk of
investing in listed companies.
BLUE-CHIP shares: high ended companies, ROI is normally higher.
- ROI:
Factors that contribute increase in share price + dividends.
Expectations of shareholders when buying shares:
o Share price increase = capital growth.
o Dividends will be generated (company pays 20% on
dividends = shareholder does NOT pay tax.)
o Combination
- Factors determining price/demand for shares:
o Level of confidence in state of economy: BULL/BEAR
o Government policies or new legislation e.g., nationalisation.
o Industry performance: strikes?
o Financial performance: sales, profits, financial ratios (solvency,
liquidity, ROI), dividends declared.
o Management and public’s confidence.
o Social issues surrounding the company e.g., eco or window
dressing.
o Legal issues, pending lawsuits or allegations e.g., price fixing
or not paying tax.
o Media coverage increased public awareness.
- Time frame:
o Long-term = no short-term need, Blue Chip.
EVALUSATING INVESTMENT OPTIONS:
1. Risk
- High investment = high returns/high loss.
- Diversification: all eggs not kept in one basket.
- Strategies to limit loss = Rebalancing: adjust your portfolio to get back
to the point where your portfolio diversifies.
2. Return on Investment (ROI)
- Measures efficiency of investment = what the investor will get back
over and above the original investment made.
3. Timeline
- Longer = greater risk can be taken e.g., if you’re 20 the you have years
to take risks.
4. Investment strategies
- Growth Strategy
Risk: high
Time: long-term
E.g.: shares
- Balanced Strategy
Risk: medium
Time: medium to long = aim is capital growth + some monthly
income.
E.g.: combination of equities = fixed deposit or rent income.
- Defensive strategy
Risk: low
Time: medium to long =aim on monthly income + some capital
growth.
E.g.: property, money in bank with smaller investment in equities.
- Conservative strategy
Risk: low to none
Time: any = aim on monthly income + maintaining capital invested.
E.g.: property ad cash instruments.
INVESTMENT OPTIONS:
EQUITY:
- Equity = shares
- Listed on JSE Ltd. = information on the shares’ performance available
for investors.
- If company is unlisted = company makes financial info available to
shareholders, banks, creditors, and SARS.
, - Options to become a shareholder are either from buying shares from
company issued the first time OR on the JSE from a previous
shareholder.
- Strategy to limit loss:
Stop-loss strategy: sell shares at predetermined price in order to stop
a loss – anything lower = deficit.
- Types of shares:
Ordinary shares:
o Holders have voting power.
o Holders’ returns come from APPRECIATION in the market value
of the shares and receiving company DIVIDENDS.
o Holders face higher risks.
Preference shares:
o Holders have NO voting power.
o Holders receive dividends BEFORE ordinary shareholders.
o Holders can claim the company’s assets BEFORE ordinary
shareholders if the companies go into liquidations.
- Risk:
High to moderate.
JSE: strict rules to protect investors and to decrease the risk of
investing in listed companies.
BLUE-CHIP shares: high ended companies, ROI is normally higher.
- ROI:
Factors that contribute increase in share price + dividends.
Expectations of shareholders when buying shares:
o Share price increase = capital growth.
o Dividends will be generated (company pays 20% on
dividends = shareholder does NOT pay tax.)
o Combination
- Factors determining price/demand for shares:
o Level of confidence in state of economy: BULL/BEAR
o Government policies or new legislation e.g., nationalisation.
o Industry performance: strikes?
o Financial performance: sales, profits, financial ratios (solvency,
liquidity, ROI), dividends declared.
o Management and public’s confidence.
o Social issues surrounding the company e.g., eco or window
dressing.
o Legal issues, pending lawsuits or allegations e.g., price fixing
or not paying tax.
o Media coverage increased public awareness.
- Time frame:
o Long-term = no short-term need, Blue Chip.