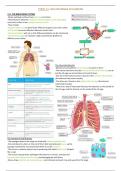
TOPIC 11: GAS EXCHANGE IN HUMANS
11.1 THE BREATHING SYSTEM
-All gas exchange surfaces have features in common
-These features allow the maximum amount of gases to be exchanged
across the surface in the smallest amount of time
-They include:
→Large surface area to allow faster diffusion of gases across the surface
→Thin walls to ensure diffusion distances remain short
→Good ventilation with air so that diffusion gradients can be maintained
→Good blood supply to maintain a high concentration gradient so
diffusion occurs faster
The Intercostal Muscles
-Muscles are only able to pull on bones, not push on them
-This means that there must be two sets of intercostal muscles; one to
pull the rib cage up and another set to pull it down.
-One set of intercostal muscles is found on the outside of the ribcage
(the external intercostal muscles)
-The other set is found on the inside of the rib cage (the internal
intercostal muscles).
-There are 2 sets of intercostal muscles: the external, on the outside of
the rib cage, and the internal, on the inside of the rib cage.
The Function of Cilia & Mucus
-The passages down to the lungs are lined with ciliated epithelial cells
-Cilia cells have tiny hairs on the end of them that beat and push mucus up the
passages towards the nose and throat where it can be removed
-The mucus is made by special mucus-producing cells called goblet cells (shaped
like a cup).
-The mucus traps particles, pathogens like bacteria or viruses, and dust and
prevents them getting into the lungs and damaging the cells there.
-Mucus traps particles, dust and pathogens and cilia beat and push it up and away from the lungs.
11.1 THE BREATHING SYSTEM
-All gas exchange surfaces have features in common
-These features allow the maximum amount of gases to be exchanged
across the surface in the smallest amount of time
-They include:
→Large surface area to allow faster diffusion of gases across the surface
→Thin walls to ensure diffusion distances remain short
→Good ventilation with air so that diffusion gradients can be maintained
→Good blood supply to maintain a high concentration gradient so
diffusion occurs faster
The Intercostal Muscles
-Muscles are only able to pull on bones, not push on them
-This means that there must be two sets of intercostal muscles; one to
pull the rib cage up and another set to pull it down.
-One set of intercostal muscles is found on the outside of the ribcage
(the external intercostal muscles)
-The other set is found on the inside of the rib cage (the internal
intercostal muscles).
-There are 2 sets of intercostal muscles: the external, on the outside of
the rib cage, and the internal, on the inside of the rib cage.
The Function of Cilia & Mucus
-The passages down to the lungs are lined with ciliated epithelial cells
-Cilia cells have tiny hairs on the end of them that beat and push mucus up the
passages towards the nose and throat where it can be removed
-The mucus is made by special mucus-producing cells called goblet cells (shaped
like a cup).
-The mucus traps particles, pathogens like bacteria or viruses, and dust and
prevents them getting into the lungs and damaging the cells there.
-Mucus traps particles, dust and pathogens and cilia beat and push it up and away from the lungs.