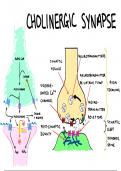
Excitatory Neurotransmitters Triggers an :
action
potential
-
Depolarisation
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters Prevents action :
potential s
Hyper polarisation
Presynaptic
Transmission of imprises
11 neurone
"Action potential reaches
many RER
end of
·Y
the presynaptic
-
lots of G the neurone
e
-C
minor
synaptic
I knob
Depolarisation of
Synaptic 2
the
presynaptic membrane
opens calcium
.
I synaptieft
ion channe a
reptationsmitte
.
3
Calcium ions diffuse into
presynaptic knob
4.
Synaptic resides
containing neurotransmitters fuse with the presynaptic membrane
S Neurotransmitter
.
diffuses across the
synaptic cleft by exocytosis
6 It binds with it's specific receptor molecule
post synaptic
.
on the membrane
-Sodium ion channels open and Nat diffuses into the postsynaptic neurone
↳Action potential is triggered
3
Cholinergic synapses Use the neurotransmitter accty, choline :
>Found in the CNS and neuromuscular
junction
Is
hydrolysed by acetylcholinesterase to produce Chlorine and ethanoic acid
Role of Synapses :
Ensure impulses are unidirectional
·Allow
divergence -> transmission into several neurones
-Allow stransmission into
convergence one neurone
Spatial Summation :
Several
Presynaptic neurones Connect to one postsynaptic neurone .
Temporal Summation One :
single presynaptic neurone releases several neurotransmitters
by several action
potentials triggered in a short period of time
Drugs Mimick the shape of the neurotransmitters
Stimulating more neurotransmitters
:
-
Blocking receptors
Central Nervous System
:
Brain and Spinal Lord
Peripheral Nervous System All that connect the CNS to the rest of the
the neurones
body
:
somatic Nervous System Nervous under conscious control
system Acetyl
:
->
choline
Autonomic Nervous under subconscious
System Nervous
system working constantly control
:
↳ Noradrenaline
↳ Sympathetic Nervous system Causes increased
activity
:
Parasympathetic Nervous Causes decreased
system activity
:
action
potential
-
Depolarisation
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters Prevents action :
potential s
Hyper polarisation
Presynaptic
Transmission of imprises
11 neurone
"Action potential reaches
many RER
end of
·Y
the presynaptic
-
lots of G the neurone
e
-C
minor
synaptic
I knob
Depolarisation of
Synaptic 2
the
presynaptic membrane
opens calcium
.
I synaptieft
ion channe a
reptationsmitte
.
3
Calcium ions diffuse into
presynaptic knob
4.
Synaptic resides
containing neurotransmitters fuse with the presynaptic membrane
S Neurotransmitter
.
diffuses across the
synaptic cleft by exocytosis
6 It binds with it's specific receptor molecule
post synaptic
.
on the membrane
-Sodium ion channels open and Nat diffuses into the postsynaptic neurone
↳Action potential is triggered
3
Cholinergic synapses Use the neurotransmitter accty, choline :
>Found in the CNS and neuromuscular
junction
Is
hydrolysed by acetylcholinesterase to produce Chlorine and ethanoic acid
Role of Synapses :
Ensure impulses are unidirectional
·Allow
divergence -> transmission into several neurones
-Allow stransmission into
convergence one neurone
Spatial Summation :
Several
Presynaptic neurones Connect to one postsynaptic neurone .
Temporal Summation One :
single presynaptic neurone releases several neurotransmitters
by several action
potentials triggered in a short period of time
Drugs Mimick the shape of the neurotransmitters
Stimulating more neurotransmitters
:
-
Blocking receptors
Central Nervous System
:
Brain and Spinal Lord
Peripheral Nervous System All that connect the CNS to the rest of the
the neurones
body
:
somatic Nervous System Nervous under conscious control
system Acetyl
:
->
choline
Autonomic Nervous under subconscious
System Nervous
system working constantly control
:
↳ Noradrenaline
↳ Sympathetic Nervous system Causes increased
activity
:
Parasympathetic Nervous Causes decreased
system activity
: