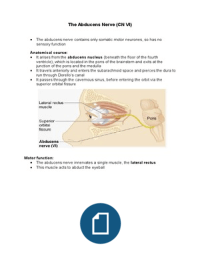
U
Market failure the
When pricemechanism leads to a misallocation of
· ->
resources
leads to
->
price mechanism a
price or
quantity that
is not
best
for society
market
- failure
live
externalities
natconsumers or
producers
---
-> costs on third parties outside the price mechanism
-esumption
externaltieparties as the results consumption of
of a
god
e
2,
g ziggarettes, alchad, driving laws No
diagram
Neg External costs
-externalities:
costs affectthird
that parties of the results production
of of
a
good
e,
g buildings, factories
inside price mechanism:Private costs (PC) -
costs of
supplying for the producer
benefits
Private (PB) benefits the
enjoyed by
-
consumer
Diagram:
Supply curve:Marginal cost
private (MPC):Lowest price thatproducer is
willing to sell their
good for
Demand curve:
Marginal private benefit (MPB):Highestprice the consumer is willing pay for to a
good
MSC
costs/ S MPC
socially
=
Benefits efficient
equilibrium
N et benefit:SB-SC welfare
I
=
welfare
loss
welfare
gain
· when MSC= MSB - welfare:0=> socially
efficient
equilibrium
P . ->
Marelibrium
I
MSC
Lost
wears on
I
s
I
Benefit
I
·n.
-
↑
I
I
D MPB MSB
=
external
=
I
CostSV ⑧ B
social
market - I
MPBMSB
=
-m
S
External cost stays 9
ea
ed
--
Q
②S
same as 0, incrast
overproduction overprodumexternal costs
social cost PC+ External costs increase as
=
- production
increases
Govt thinks of
↳ social benefits:PB External Benefits +
for neg externalities social benefit PB 0
=
+
-> SB: PB MSB:MPB =
external benefit 0 =
Market failure the
When pricemechanism leads to a misallocation of
· ->
resources
leads to
->
price mechanism a
price or
quantity that
is not
best
for society
market
- failure
live
externalities
natconsumers or
producers
---
-> costs on third parties outside the price mechanism
-esumption
externaltieparties as the results consumption of
of a
god
e
2,
g ziggarettes, alchad, driving laws No
diagram
Neg External costs
-externalities:
costs affectthird
that parties of the results production
of of
a
good
e,
g buildings, factories
inside price mechanism:Private costs (PC) -
costs of
supplying for the producer
benefits
Private (PB) benefits the
enjoyed by
-
consumer
Diagram:
Supply curve:Marginal cost
private (MPC):Lowest price thatproducer is
willing to sell their
good for
Demand curve:
Marginal private benefit (MPB):Highestprice the consumer is willing pay for to a
good
MSC
costs/ S MPC
socially
=
Benefits efficient
equilibrium
N et benefit:SB-SC welfare
I
=
welfare
loss
welfare
gain
· when MSC= MSB - welfare:0=> socially
efficient
equilibrium
P . ->
Marelibrium
I
MSC
Lost
wears on
I
s
I
Benefit
I
·n.
-
↑
I
I
D MPB MSB
=
external
=
I
CostSV ⑧ B
social
market - I
MPBMSB
=
-m
S
External cost stays 9
ea
ed
--
Q
②S
same as 0, incrast
overproduction overprodumexternal costs
social cost PC+ External costs increase as
=
- production
increases
Govt thinks of
↳ social benefits:PB External Benefits +
for neg externalities social benefit PB 0
=
+
-> SB: PB MSB:MPB =
external benefit 0 =