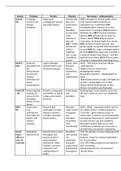
Calorimetry
Aim:
The aim of the experiment is to determine the physical changes and temperature change and study the
cooling curve of stearic acid and Paraffin wax.
Introduction:
Within this assignment, I will be using standard laboratory equipment and techniques to carry out
calorimetry. I will use the measurement of temperature to determine the cooling curve for stearic acid and
paraffin wax.
Stearic acid is employed in the manufacture of candles, cosmetics, shaving soaps, lubricants, and
pharmaceuticals. In nature, stearic acid occurs primarily as a mixed triglyceride, or fat, with other long-
chain acids and as an ester of a fatty alcohol.
Paraffin wax is a familiar substance because it is used to make candles. It is a soft, white solid at room
temperature that melts and burns easily. Its chemical composition is a mix of hydrocarbon molecules
known as alkanes.
Calibration of thermometers:
Boiling water Ice water
1. Get a beaker and your thermometer 1. Get a beaker and fill with fresh ice.
2. Boil the kettle 2. Add a sprinkle of salt onto the ice
3. Tip the boiling water into beaker (don’t 3. Add water to the beaker
touch glass beaker while doing it) 4. Place thermometer into the beaker and
4. Place thermometer into water and measure the temperature of the water.
measure the temperature. 5. The reading should be 0°C or close or
5. Read the temperature (should be close to below 0 °C
100°C)
Results from calibration:
Analogue boiling water Digital boiling water (°C) Analogue ice water (°C) Digital ice water (°C)
(°C)
94.9 88.1 0.2 1.3
95.1 94.31 0.1 2.9
95 96.3 0.1 0.6
Mean=95 Mean=92.90 Mean=0.1 Mean=1.6
The analogue results are more precise and are closer together in results while the digital are more
scattered. For analogue, the results were closer to 100°C and 0°C. Thus making the analogue more accurate
and reliable for use.
Ice water:
When the salt was added to the ice, salt first dissolves in the film of liquid water that is always present on
the surface, thereby lowering its freezing point below the ices temperature, thus this improves the
accuracy experiment.
Boiling water:
As there were students in the laboratory and to make the experiment more safe, kettles were used when
calibrating the thermometers, however to improve the experiment a Bunsen burner could have been used
to boil the water to get to 100°C as the kettle water does not reach to 100°C.
When determining the thermometer to use me chose the analogue thermometer as when calibrating the
mean for the analogue thermometer was closer to boiling point of water and 0 C.
1
, Equipment list:
Boiling tube with stearic acid
Boiling tube with paraffin wax
Stop clock
Digital thermometer
Analogue thermometer
Test tube rack
250ml beaker
Ice
Method:
1. With your partner, either go to the stearic acid or paraffin wax water baths and measure the
temperature of the water bath.
2. The analogue thermometer was placed into one of the boiling tubes and the temperature was
measured
3. For every temperature drop by 1°c, the time was recorded.
4. Once the wax temperature reached room temperature, it was placed back into the water bath.
5. The thermometer was left in until the stearic acid/paraffin wax was melted, then removed.
Results: Paraffin wax
Time min Temperature °c
0.00 65
0.06 64
0.22 63
0.39 62
1.02 61
1.29 60
2.29 59
3.29 58
4.32 57
5.38 56
6.56 55
7.42 54
8.43 53
9.32 52
10.24 51
11.03 50
11.40 49
11.55 48
12.19 47
12.50 46
13.21 45
13.56 44
14.40 43
15.16 42
15.47 41
16.13 40
2
Aim:
The aim of the experiment is to determine the physical changes and temperature change and study the
cooling curve of stearic acid and Paraffin wax.
Introduction:
Within this assignment, I will be using standard laboratory equipment and techniques to carry out
calorimetry. I will use the measurement of temperature to determine the cooling curve for stearic acid and
paraffin wax.
Stearic acid is employed in the manufacture of candles, cosmetics, shaving soaps, lubricants, and
pharmaceuticals. In nature, stearic acid occurs primarily as a mixed triglyceride, or fat, with other long-
chain acids and as an ester of a fatty alcohol.
Paraffin wax is a familiar substance because it is used to make candles. It is a soft, white solid at room
temperature that melts and burns easily. Its chemical composition is a mix of hydrocarbon molecules
known as alkanes.
Calibration of thermometers:
Boiling water Ice water
1. Get a beaker and your thermometer 1. Get a beaker and fill with fresh ice.
2. Boil the kettle 2. Add a sprinkle of salt onto the ice
3. Tip the boiling water into beaker (don’t 3. Add water to the beaker
touch glass beaker while doing it) 4. Place thermometer into the beaker and
4. Place thermometer into water and measure the temperature of the water.
measure the temperature. 5. The reading should be 0°C or close or
5. Read the temperature (should be close to below 0 °C
100°C)
Results from calibration:
Analogue boiling water Digital boiling water (°C) Analogue ice water (°C) Digital ice water (°C)
(°C)
94.9 88.1 0.2 1.3
95.1 94.31 0.1 2.9
95 96.3 0.1 0.6
Mean=95 Mean=92.90 Mean=0.1 Mean=1.6
The analogue results are more precise and are closer together in results while the digital are more
scattered. For analogue, the results were closer to 100°C and 0°C. Thus making the analogue more accurate
and reliable for use.
Ice water:
When the salt was added to the ice, salt first dissolves in the film of liquid water that is always present on
the surface, thereby lowering its freezing point below the ices temperature, thus this improves the
accuracy experiment.
Boiling water:
As there were students in the laboratory and to make the experiment more safe, kettles were used when
calibrating the thermometers, however to improve the experiment a Bunsen burner could have been used
to boil the water to get to 100°C as the kettle water does not reach to 100°C.
When determining the thermometer to use me chose the analogue thermometer as when calibrating the
mean for the analogue thermometer was closer to boiling point of water and 0 C.
1
, Equipment list:
Boiling tube with stearic acid
Boiling tube with paraffin wax
Stop clock
Digital thermometer
Analogue thermometer
Test tube rack
250ml beaker
Ice
Method:
1. With your partner, either go to the stearic acid or paraffin wax water baths and measure the
temperature of the water bath.
2. The analogue thermometer was placed into one of the boiling tubes and the temperature was
measured
3. For every temperature drop by 1°c, the time was recorded.
4. Once the wax temperature reached room temperature, it was placed back into the water bath.
5. The thermometer was left in until the stearic acid/paraffin wax was melted, then removed.
Results: Paraffin wax
Time min Temperature °c
0.00 65
0.06 64
0.22 63
0.39 62
1.02 61
1.29 60
2.29 59
3.29 58
4.32 57
5.38 56
6.56 55
7.42 54
8.43 53
9.32 52
10.24 51
11.03 50
11.40 49
11.55 48
12.19 47
12.50 46
13.21 45
13.56 44
14.40 43
15.16 42
15.47 41
16.13 40
2