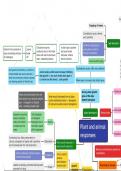
Dropping of leaves
Controlled by auxin, ethene
and cytokinins
Leaf abscission
Cytokinins (produced in
Cellulose enzymes As leaf ages cytokinin
Suberin forms protective Leaves young leaves (sink for
produced due to this break and auxin levels
layer preventing entrance break transport in phloem)
down cell wall in abscission decrease, ethene
of pathogens off
layer -weakening leaves leaves increase
Auxin prevents aging F
e
Controlled by auxins, ABA and cytokinins a
Bud growth promoted by cytokinins (
Auxins levels as ABA levels increase (inhibiting p
concentrated near auxin reserves) -
side growth) -> low auxin levels when apex is b
when bud removed cytokinins spread
cut mean low ABA levels (.: side growth) When apex is removed, side shoots grow.
out allowing growth of lateral buds
During shoot growth- Cerebrum
When shoot illuminated from one grow of the side
When shoot illuminated from all sides
side (auxins move towards shaded doesnt take place
(auxins distributed evenly -> elongation
part -> elongation of shaded
of cells across entire zone of elongation)
side -> bending towards light
The cereb
Apical dominance Human brain
Expansins (enzyme) Cell elongation
loosens cellulose - via transport
make cells stretch hydrogen ions to Auxins Hypothala
to make room for
water
cell walls- lowers
pH for expansins
Plant and animal
Commercial use: delay senescence in responses Medulla o
citruses, elongation of apples with cytokinins Gibberellins Plant growth responses ->
and in brewing beer for malt production plant growth regulators
Nervous and endocrine systems in
prevent yellowing of lettuce leaves - Shoots exhibit coordination
Cytokinins
promote shoot growth positive
phototropism -
speeds up ripening, promote lateral growth, towards light growth Physiological changes Pu
Ethene
promote fruit drop response Phototropism