Bio
YEAR 1
, Testing for all
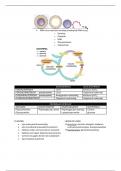
Carbohydrate,sugar=benedict's test-reducing sugar=add benedicts which is blue,
heat sample in water bath to 100c, if is positive will turn red
Non reducing sugar-after testing for reducing sugar, add hcl, boil in water bath,
test again if it turns red then non reducing sugar present if stays blue no sugar
Emulsion test Lipids
Mix substance with ethanol
Add water
Milky layer then lipid is present.
Biuret test Proteins, biuret is made up of copper sulfate and naoh
Add biuret solution to sample
Goes from blue to purple protein is present, if not remains it Blue
,Carbohydrates Remember alpha
glucose by sAntA
HO HO same side
C6H1206 is the general formula
Monosaccharide + monosaccharide = disaccharide
Glucose + glucose= maltose
This is alpha glucose
Glucose + fructose = sucrose beta glucose is when the
OH is on the opposite
Glucose + galactose = lactose all sugars end here
Polysaccharides are made by condensation reaction
E.G. unbranched-cellulose,Beta glucose, in cell wall; rest are alpha glucose
Amylose and Amylopectin= glucose in starch
Glycogen stores starch (animals rest are in plants) very branched more SA for respiration
All have glycosidic bonds. And hydrogen bonds
,Triglyceride structure
Lipids Phospholipids structure
+ 3h20
Phosphate group bonded on O of glycerol
Glycerol 3 fatty acids Triglyceride 2 fatty acid chains bonded to glycerol
Phosphate head is hydrophilic
Fatty acid tails are hydrophobic
Glycerol and 3 fatty acids join together by ester bonds The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer
via a condensation reaction. They can be saturated or Hydrophobic tail faces inwards
unsaturated. Middle is hydrophobic which makes it hard for H20 to
Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds between diffuse in fast
carbons and can cause increase in cholesterol.
Unsaturated fatty acids have double bonds between
carbons and hence less hydrogen.
Function= energy storage Long polymers hence lots of bonds has
hydrophobic tails on inside hence no effects on osmosis
YEAR 1
, Testing for all
Carbohydrate,sugar=benedict's test-reducing sugar=add benedicts which is blue,
heat sample in water bath to 100c, if is positive will turn red
Non reducing sugar-after testing for reducing sugar, add hcl, boil in water bath,
test again if it turns red then non reducing sugar present if stays blue no sugar
Emulsion test Lipids
Mix substance with ethanol
Add water
Milky layer then lipid is present.
Biuret test Proteins, biuret is made up of copper sulfate and naoh
Add biuret solution to sample
Goes from blue to purple protein is present, if not remains it Blue
,Carbohydrates Remember alpha
glucose by sAntA
HO HO same side
C6H1206 is the general formula
Monosaccharide + monosaccharide = disaccharide
Glucose + glucose= maltose
This is alpha glucose
Glucose + fructose = sucrose beta glucose is when the
OH is on the opposite
Glucose + galactose = lactose all sugars end here
Polysaccharides are made by condensation reaction
E.G. unbranched-cellulose,Beta glucose, in cell wall; rest are alpha glucose
Amylose and Amylopectin= glucose in starch
Glycogen stores starch (animals rest are in plants) very branched more SA for respiration
All have glycosidic bonds. And hydrogen bonds
,Triglyceride structure
Lipids Phospholipids structure
+ 3h20
Phosphate group bonded on O of glycerol
Glycerol 3 fatty acids Triglyceride 2 fatty acid chains bonded to glycerol
Phosphate head is hydrophilic
Fatty acid tails are hydrophobic
Glycerol and 3 fatty acids join together by ester bonds The cell membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer
via a condensation reaction. They can be saturated or Hydrophobic tail faces inwards
unsaturated. Middle is hydrophobic which makes it hard for H20 to
Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds between diffuse in fast
carbons and can cause increase in cholesterol.
Unsaturated fatty acids have double bonds between
carbons and hence less hydrogen.
Function= energy storage Long polymers hence lots of bonds has
hydrophobic tails on inside hence no effects on osmosis