The Human Immunodeficiency Virus
=
HIV
→
causes the disease acquired immune
deficiency syndrome ( AIDS ) .
AIDS is condition where the immune deteriorates and
eventually fails This makes someone with
system
a
-
.
AIDS more vulnerable to other infections , like pneumonia .
What are the host cells for HIV ?
HIV CD4X cells , cells that have specific CD4 their
targets meaning this molecule called
-
on
membrane I CD4 is used to help
:m→:tf
.
immune cells communicates CD4X cells
÷
→ ~
9 9 ,• dendritic
\
- -
, ?
a•
,• cells
-
,
. .
r -
O
B- too
ai /
I
B- hoo n
• ↳
• b.
%
• "
r
macrophage
HIV infects and
eventually kills helper T cells ( a CD4X cell )
-
-
.
•
The CD4 -1 cells ( Tn cells ) act as hosts cells
e.g
-
Remember helper ( via called
T send chemical signals molecules
cytokines) that activate
-
cells
phagocytes ( macrophages Ineutrophils ) ,
cytotoxic T-cells and B- cells .
How does HIV
develop AIDS ?
Without T-cells
enough helper (due
hijacking helper T-cells) the
system unable have
-
to HIV ,
immune is to
effective infections because don't behave how
an
response to other immune
system cells
they should .
People infected with HIV develop AIDS when the helper T their
body reach
-
-
cell numbers in a
low level
critically .
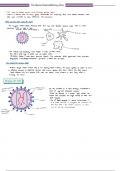
Structure of HIV
,*.. :* .
.io/gq
Bo
Of
mate attachment
genetic µ ,
protein
'
On the outside is a
lipid envelope ,
embedded in
g•
⑧
( RNA
) which are -
like attachment proteins
✓ peg
⑧⑧\ food Inside the
.
, envelope is a
protein layer called the
capsid that encloses two
single strands of RNA and
IE 3. cars .
÷:÷÷÷::÷÷:c:*:*:c:*:÷:
Bol n
hope DNA from RNA -
the reverse reaction to that
too carried
r
by transcriptase )
Boo
out
lipid envelope
& &
r
reverse
B
transcriptase
(enzyme )
matrix
=
HIV
→
causes the disease acquired immune
deficiency syndrome ( AIDS ) .
AIDS is condition where the immune deteriorates and
eventually fails This makes someone with
system
a
-
.
AIDS more vulnerable to other infections , like pneumonia .
What are the host cells for HIV ?
HIV CD4X cells , cells that have specific CD4 their
targets meaning this molecule called
-
on
membrane I CD4 is used to help
:m→:tf
.
immune cells communicates CD4X cells
÷
→ ~
9 9 ,• dendritic
\
- -
, ?
a•
,• cells
-
,
. .
r -
O
B- too
ai /
I
B- hoo n
• ↳
• b.
%
• "
r
macrophage
HIV infects and
eventually kills helper T cells ( a CD4X cell )
-
-
.
•
The CD4 -1 cells ( Tn cells ) act as hosts cells
e.g
-
Remember helper ( via called
T send chemical signals molecules
cytokines) that activate
-
cells
phagocytes ( macrophages Ineutrophils ) ,
cytotoxic T-cells and B- cells .
How does HIV
develop AIDS ?
Without T-cells
enough helper (due
hijacking helper T-cells) the
system unable have
-
to HIV ,
immune is to
effective infections because don't behave how
an
response to other immune
system cells
they should .
People infected with HIV develop AIDS when the helper T their
body reach
-
-
cell numbers in a
low level
critically .
Structure of HIV
,*.. :* .
.io/gq
Bo
Of
mate attachment
genetic µ ,
protein
'
On the outside is a
lipid envelope ,
embedded in
g•
⑧
( RNA
) which are -
like attachment proteins
✓ peg
⑧⑧\ food Inside the
.
, envelope is a
protein layer called the
capsid that encloses two
single strands of RNA and
IE 3. cars .
÷:÷÷÷::÷÷:c:*:*:c:*:÷:
Bol n
hope DNA from RNA -
the reverse reaction to that
too carried
r
by transcriptase )
Boo
out
lipid envelope
& &
r
reverse
B
transcriptase
(enzyme )
matrix