GCSE Biology- Respira3on/ Gas exchange
2.46
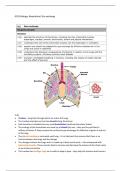
• Trachea – long tube through which air enters the lungs
• The trachea branches out into two bronchi (sing. Bronchus)
• Each bronchus is divided into very small bronchioles (small sub-branches/ tubes)
• The endings of the bronchioles are made up of alveoli (air sacs – they are tiny and there’s
millions of them) à they increase the surface for gas exchange/ for diffusion of gases in and out
of the lings
• The pleural membrane surrounds each lung – it is a lubricant that ensures that there is no
friction between the lungs and the ribcage
• The ribcage encloses the lungs and it is made up of bone and muscle – ribs interspaced with
intercostal muscles. These muscles help to increase and decrease the volume of the chest cavity
as we inhale and exhale
• The trachea has cartilage rings on its walls to keep it open – they help the trachea resist tension
2.46
• Trachea – long tube through which air enters the lungs
• The trachea branches out into two bronchi (sing. Bronchus)
• Each bronchus is divided into very small bronchioles (small sub-branches/ tubes)
• The endings of the bronchioles are made up of alveoli (air sacs – they are tiny and there’s
millions of them) à they increase the surface for gas exchange/ for diffusion of gases in and out
of the lings
• The pleural membrane surrounds each lung – it is a lubricant that ensures that there is no
friction between the lungs and the ribcage
• The ribcage encloses the lungs and it is made up of bone and muscle – ribs interspaced with
intercostal muscles. These muscles help to increase and decrease the volume of the chest cavity
as we inhale and exhale
• The trachea has cartilage rings on its walls to keep it open – they help the trachea resist tension