Coordination of The
Cardiac Cycle
Myocytes (myogenic cells) = polarised cells that initiate their own contraction
Purkyene tissue = muscle fibres that conduct the wave of excitation
Myocytes have a slight charge across their membrane (polarised)
Allows them to be affected by the wave of excitation
When the charge is reversed, they become depolarised
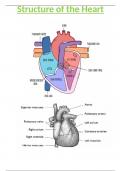
Depolarisation occurs in the sino-atrial node (SAN) in the right atrium
SAN is controlled by the nervous system
Membrane around the node allows charge to be maintained:
o Positive inside
o Negative outside
Caused by ions building up
During depolarisation, positive ions move outside
Repolarisation is when ions move to even the charge across the membrane
Atrial Systole
SAN sends a wave of electrical activity through the atria (wave of excitation)
As the wave of excitation passes through the atrial walls, they contract in synchrony
Non-conductive tissue between chambers prevent ventricles from contracting
Ventricular Systole
Electrical wave reaches atrio-ventricular node (AVN) which relays the wave down the
inter-ventricular septum (IVS) through purkyene tissue
As the wave of excitation passes through the ventricular walls, they contract in
synchrony from the bottom upwards
Cardiac Cycle
Myocytes (myogenic cells) = polarised cells that initiate their own contraction
Purkyene tissue = muscle fibres that conduct the wave of excitation
Myocytes have a slight charge across their membrane (polarised)
Allows them to be affected by the wave of excitation
When the charge is reversed, they become depolarised
Depolarisation occurs in the sino-atrial node (SAN) in the right atrium
SAN is controlled by the nervous system
Membrane around the node allows charge to be maintained:
o Positive inside
o Negative outside
Caused by ions building up
During depolarisation, positive ions move outside
Repolarisation is when ions move to even the charge across the membrane
Atrial Systole
SAN sends a wave of electrical activity through the atria (wave of excitation)
As the wave of excitation passes through the atrial walls, they contract in synchrony
Non-conductive tissue between chambers prevent ventricles from contracting
Ventricular Systole
Electrical wave reaches atrio-ventricular node (AVN) which relays the wave down the
inter-ventricular septum (IVS) through purkyene tissue
As the wave of excitation passes through the ventricular walls, they contract in
synchrony from the bottom upwards