ECG Tachyarrhythmias
Definition Tachycardia: Heart rates >100bpm
ECG characteristics
QRS
o Wide vs Narrow complex
Regular vs Irregular
P waves
Narrow complex tachycardias Wide complex tachycardias
Action potential starts in the atria Action potential starts in the
ventricle
Atrial fibrilation Ventricular tachycardias
Irregular
Atrial flutter Supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy
Sinus tachycardia Supraventricular tachycardia with pre-
AV-Nodal Re-entry Tachycardia (AVNRT) excitation
AV Re-entry Tachycardia (AVRT) e.g. Wolf-Parkinson-White
Identify the origin of the beat (Chapter conduction diseases)
Sinus beat
Atrial beat
Junctional (AV nodal) beats
Ventricular beats
, Atrial Fibrillation Disorganised activation of the atria
No P waves
Irregular ventricular rate
Most common sustained arrhythmia
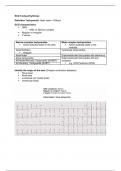
Atrial Fibrilation on ECG
Irregularly irregular rhythm First differential must be atrial fibrilation
No P waves
Unstable baseline (fine and coarse fibrilation waves)
Narrow QRS
o Unless other conduction pathology present
Definition Tachycardia: Heart rates >100bpm
ECG characteristics
QRS
o Wide vs Narrow complex
Regular vs Irregular
P waves
Narrow complex tachycardias Wide complex tachycardias
Action potential starts in the atria Action potential starts in the
ventricle
Atrial fibrilation Ventricular tachycardias
Irregular
Atrial flutter Supraventricular tachycardia with aberrancy
Sinus tachycardia Supraventricular tachycardia with pre-
AV-Nodal Re-entry Tachycardia (AVNRT) excitation
AV Re-entry Tachycardia (AVRT) e.g. Wolf-Parkinson-White
Identify the origin of the beat (Chapter conduction diseases)
Sinus beat
Atrial beat
Junctional (AV nodal) beats
Ventricular beats
, Atrial Fibrillation Disorganised activation of the atria
No P waves
Irregular ventricular rate
Most common sustained arrhythmia
Atrial Fibrilation on ECG
Irregularly irregular rhythm First differential must be atrial fibrilation
No P waves
Unstable baseline (fine and coarse fibrilation waves)
Narrow QRS
o Unless other conduction pathology present