ECG basics
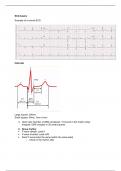
Example of a normal ECG
Intervals
Large square: 200ms
Small square: 40ms, 1mm x1mm
1. Heart rate: Number of QRS complexes * 6 (Count in the rhythm strip)
Irregular: QRS complex in 30 small squares
2. Sinus rhythm
P wave upright: Lead II
P wave inverted: Lead aVR
Each P wave looks the same (within the same lead)
o Check in the rhythm strip
, 3. Heart axis
Assess whether QRS complex is positive or negative:
Always compare to the T-P segment
o The part between the T wave of the last beat and the P wave of the next beat
Heart Axis assesment
Intermediate
o Lead I: Positive
o Lead II: Positive
Left
o Lead I: Positive
o Lead II: Negative
Right
o Lead I: Negative
o aVF: Positive
Extreme
o Lead I: Negative
o aVF: Negative
Example of a normal ECG
Intervals
Large square: 200ms
Small square: 40ms, 1mm x1mm
1. Heart rate: Number of QRS complexes * 6 (Count in the rhythm strip)
Irregular: QRS complex in 30 small squares
2. Sinus rhythm
P wave upright: Lead II
P wave inverted: Lead aVR
Each P wave looks the same (within the same lead)
o Check in the rhythm strip
, 3. Heart axis
Assess whether QRS complex is positive or negative:
Always compare to the T-P segment
o The part between the T wave of the last beat and the P wave of the next beat
Heart Axis assesment
Intermediate
o Lead I: Positive
o Lead II: Positive
Left
o Lead I: Positive
o Lead II: Negative
Right
o Lead I: Negative
o aVF: Positive
Extreme
o Lead I: Negative
o aVF: Negative