Lecture 7: Anatomy Urinary system
Three Functions of the Urinary System
• Excretion
– Removal of organic wastes from body fluids
• Elimination
– Discharge of waste products
• Homeostatic regulation
– Of blood plasma volume and solute concentration
urethra longer in males
Position (big muscles protect the kidney)
- Between T12-L3
- Left higher (because on the right side you have your liver)
,Looking behind the peritoneum (abdominal cavity); arteries posterior to veins; fatty tissue to make
sure the kidney stays in the right place.
,Kidney> fibrous capsule> perinephric fat> renal fascia
• Atrophy of fatty tissue around the kidney (too little fatty tissue e.g., anorexia)
– floating kidney (kidney can move when you stand up or sit down)
– nephroptosis
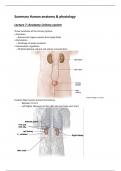
, Kidney
• Renal hilum
– Renal artery
– Renal vein
– ureter (renal pelvis)
• Fibrous capsule
• Renal cortex
Posterior vieuw