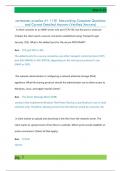
Atomic structure:
Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons.
Protons are positively charged, neutrons are uncharged, and electrons
are negatively charged.
The atomic number indicates the number of protons in the atom and the
mass number indicates the sum of protons and neutrons.
Periodic table:
The periodic table is organized in order of increasing atomic number,
divided into periods (rows) and groups (columns).
Elements of the same group have similar chemical properties, and
elements of the same age have the same number of electron shells.
Compound:
When an electron moves from one atom to another, an ionic bond is
formed between the atoms, creating an ion with the opposite charge.
A covalent bond is formed when atoms share electrons. They can be
nonpolar (evenly distributed) or polar (unevenly distributed).
Stoichiometry:
Stoichiometry is the study of quantitative relationships between
reactants and products in chemical reactions.
A balanced chemical equation gives the stoichiometric ratio of reactants
and products. The concept of moles is used for conversions between
masses, moles and particles (Avogadro's number:
6.022x10^23).
Acids and Bases:
Acids release hydrogen ions (H+) in water and bases release hydroxide
ions (OH-).
A pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution. pH 7 7 is basic
and pH=7 is neutral.
Chemical reaction:
Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons.
Protons are positively charged, neutrons are uncharged, and electrons
are negatively charged.
The atomic number indicates the number of protons in the atom and the
mass number indicates the sum of protons and neutrons.
Periodic table:
The periodic table is organized in order of increasing atomic number,
divided into periods (rows) and groups (columns).
Elements of the same group have similar chemical properties, and
elements of the same age have the same number of electron shells.
Compound:
When an electron moves from one atom to another, an ionic bond is
formed between the atoms, creating an ion with the opposite charge.
A covalent bond is formed when atoms share electrons. They can be
nonpolar (evenly distributed) or polar (unevenly distributed).
Stoichiometry:
Stoichiometry is the study of quantitative relationships between
reactants and products in chemical reactions.
A balanced chemical equation gives the stoichiometric ratio of reactants
and products. The concept of moles is used for conversions between
masses, moles and particles (Avogadro's number:
6.022x10^23).
Acids and Bases:
Acids release hydrogen ions (H+) in water and bases release hydroxide
ions (OH-).
A pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution. pH 7 7 is basic
and pH=7 is neutral.
Chemical reaction: