·
vocal cords divide upper and lower
respiratory tract.
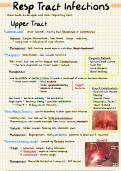
Upper Tract
·
Common Cold:virus-caused, mainly by a Rhinovirus or Coronavirus.
Features:Coryza/Rhinnorhoea, Sore throat,
cough, sneezing.
·
runny nose is indicative of viral infection
Management:Self-limiting, avoid children (Reye's Syndrome).
·
aspirin in
·Pharyngitis:sore throat, can include tonsillitis.
Diagnosis Methods.
90% viral, but look out for and Fusobacterium.
Strep A sputum/blood culture
· -
bacteria diagnosed swab culture.
via throat Swab PCR
-
+
Urine
Antigens
-
Management:
-
Blood Serology
·
use FeverPAIN or Centor criteria to predictlikelihood of viral vs. bacteria infection.
these scores assess: tonsil exudate
(Yea
-
-tenderlymphadenopathy
absence of cough complications:
Strep A
-
-
fever -
Paratonsillar Abscess
(auinsy)
low score bacteria
=
unlikely
-
no antibiotics -
Fever
Scarlet
high score bacteria
likely-consider antibiotics Rheumatic Fever/
= -
Strep A 10
day course Benicillin. Heart Disease
=
Glomerulonephritis
-
·
Otitis Media/Sinusitis:can be
secondary to other infection.
upper tract
mostly viral, but look outfor Strep pneumococcus.
·
Pneumococcus invade
meninges from causing meningitis.
·
can sinus,
Features:tender sinuses, hearing loss, dizziness, pain. STREP A
·
Management:degongestant, rarely antibiotics, grommet to drain pus it recurrent.
·
QUINSY
Pertussis (Whooping Cough):caused by Pertussis bacteria.
·
stages:1. Catarrhal:Coryza, highly infections.
·
2.
Paroxysmal:weeks of intense coughing.
3. Convalescent:chronic
cough.
·
Management:Macrolide Antibiotics (-omycin), DTP Vaccine.