VARICOSE VEINS
Varicose veins = dilated, superficial veins found mostly in the lower limb, measuring >3mm in diameter.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Presentation
§ Unsightly, visible and distended veins
§ Heavy or dragging sensation in legs
§ Discolouration of the skin ® haemosiderin deposition
§ Aching
§ Itching
§ Oedema
§ Muscle cramps
§ Restless legs
§ Skin changes ® varicose eczema
§ Ulceration
§ Thrombophlebitis
§ Bleeding ® often post-trauma.
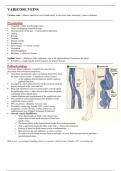
Saphena Varix ® dilatation of the saphenous vein at the saphenofemoral junction in the groin.
§ It displays a cough impulse (often mistaken for femoral hernia).
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Pathophysiology
Torturous, dilated segments of superficial veins that are
associated with valvular incompetence.
§ Arise from incompetent valves, permitting blood flow from
the deep venous system ® superficial venous system
o At the sapheno-femoral junction and the sapheno-
popliteal junction
§ Incompetent valves allow blood to be drawn downwards by
gravity and pool in the veins and feet
§ Deep and superficial veins are connected by vessels called
the perforating veins ® allow blood to flow from deep into
superficial and overloads them
§ Causes dilatation and engorgement of the superficial veins
§ This results in venous hypertension and dilatation of the
superficial venous system
§ 98% are primary idiopathic varicose veins
§ Secondary causes may include: DVT, pelvic masses
(pregnancy, uterine fibroids, ovarian masses) or AV
malformations (e.g. Klippel-Trenaunay Syndrome)
§ Chronic venous insufficiency
o When blood pools in distal veins, the pressure
causes them to leak small amounts of blood into
nearby tissue
o The haemoglobin in the leaked blood breaks down to haemosiderin
o This is deposited around the shins in the legs ® brown discolouration
o Pooling of blood in distal tissues results in inflammation
o Skin becomes dry and inflamed ® venous eczema
o The skin and soft tissues become fibrotic and tight ® lower limbs become narrow and hard =
lipodermatosclerosis.
Risk factors ® prolonged standing, obesity, pregnancy, family history, female, DVT, increasing age.
Varicose veins = dilated, superficial veins found mostly in the lower limb, measuring >3mm in diameter.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Presentation
§ Unsightly, visible and distended veins
§ Heavy or dragging sensation in legs
§ Discolouration of the skin ® haemosiderin deposition
§ Aching
§ Itching
§ Oedema
§ Muscle cramps
§ Restless legs
§ Skin changes ® varicose eczema
§ Ulceration
§ Thrombophlebitis
§ Bleeding ® often post-trauma.
Saphena Varix ® dilatation of the saphenous vein at the saphenofemoral junction in the groin.
§ It displays a cough impulse (often mistaken for femoral hernia).
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Pathophysiology
Torturous, dilated segments of superficial veins that are
associated with valvular incompetence.
§ Arise from incompetent valves, permitting blood flow from
the deep venous system ® superficial venous system
o At the sapheno-femoral junction and the sapheno-
popliteal junction
§ Incompetent valves allow blood to be drawn downwards by
gravity and pool in the veins and feet
§ Deep and superficial veins are connected by vessels called
the perforating veins ® allow blood to flow from deep into
superficial and overloads them
§ Causes dilatation and engorgement of the superficial veins
§ This results in venous hypertension and dilatation of the
superficial venous system
§ 98% are primary idiopathic varicose veins
§ Secondary causes may include: DVT, pelvic masses
(pregnancy, uterine fibroids, ovarian masses) or AV
malformations (e.g. Klippel-Trenaunay Syndrome)
§ Chronic venous insufficiency
o When blood pools in distal veins, the pressure
causes them to leak small amounts of blood into
nearby tissue
o The haemoglobin in the leaked blood breaks down to haemosiderin
o This is deposited around the shins in the legs ® brown discolouration
o Pooling of blood in distal tissues results in inflammation
o Skin becomes dry and inflamed ® venous eczema
o The skin and soft tissues become fibrotic and tight ® lower limbs become narrow and hard =
lipodermatosclerosis.
Risk factors ® prolonged standing, obesity, pregnancy, family history, female, DVT, increasing age.