- Temperature
- Glucose levels
- Solute potential
importance of dynamic equilibrium – around set point
- body cells function efficiently – constant & appropriate rate
- conditions of body cell don’t fluctuate with external environment
- biochemical reactions require specific conditions = constant – even during activity
- enzyme optimum
- water potential – don’t plasmolyse
b. negative feedback: restore conditions to set point
receptor – detects change + signal to coordinator (temperature receptor)
control centre – detect signal from receptor + coordinates response via effector (hypothalamus)
effector – bring about response to restore to set point (muscle/gland)
positive feedback: increases change
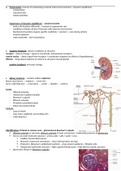
c. kidney structure – contains million nephrons
blood: renal artery → nephron → renal vein
urine: collecting duct → renal pelvis → ureter → bladder → urethra
Cortex
- Afferent arteriole
- Glomerulus (capillary bundle)
- Bowman’s capsule
- Efferent arteriole
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Distal convoluted tubule
Medulla
- Loop of Henlé
- Vasa recta: capillaries surrounding LoH
- Collecting duct
Ultrafiltration of blood to remove urea – glomerulus & Bowman’s capsule
afferent arteriole to narrower efferent arteriole & heart contraction = hydrostatic pressure in glomerulus
forces out small molecules: glucose / amino acids / salts / water / urea
Capillary fenestrations/pores
Bowman’s basement membrane – sieve (cells/proteins too big)
Podocyte’s (Bowman’s epithelium) pedicels – wrap around capillaries = filtration slits
Glomerulus hydrostatic pressure > high capsule fluid pressure + high plasma osmotic pressure
= glomerular filtrate in Bowman’s capsule
, d. kidney functions
Osmoregulation: control of water & solutes in bodily fluids (tissue fluid / blood / lymph)
Excretion: removal of metabolic waste products
- excess amino acids deaminated in liver (can’t be stored)
- amino group → ammonia → urea (less toxic) (transported to blood plasma to kidney)
e. Selective reabsorption – proximal convoluted tubule → peritubular capillaries
of filtrate’s required molecules into blood = filtrate isotonic with blood plasma
all glucose & amino acids = Na+ co-transport (facilitated diffusion) – secondary active transport
up to glucose threshold: max pct can reabsorb (limited by carrier proteins) – rest remains in filtrate → urine
most water = osmosis – Na+ (co transport) lower blood’s water potential
most mineral ions = active transport
some filtered proteins + some urea = diffusion
Proximal convoluted tubule adaptations
- large SA – for reabsorption
o Nephrons: long & millions per kidney
o Cuboidal epithelium: microvilli + basal channels (folds facing capillary)
- Many mitochondria – ATP for active transport
- Tight junctions – prevent reabsorbed materials seeping back to filtrate
- Close to capillaries – short diffusion pathway & increase concentration gradient
Osmoregulation: prevent cells bursting & maintain solute concentrations (enzymes/metabolites)
- ascending limb – impermeable: actively transport Na +/Cl- out filtrate → medulla tissue fluid = salty
- descending limb – permeable: water osmoses out filtrate → medulla tissue fluid
= filtrate most concentrated at loop apex
hair-pin: counter-current multiplier – max concentration at loop apex (& higher in medulla)
- collecting duct: water osmoses out (to concentrated medulla tissue fluid – always higher so osmosis continues)
o filtrate hypertonic to blood = urine
- water reabsorbed → vasa recta blood
f. endocrine glands: secrete hormones for negative feedback
ADH produced by hypothalamus & secreted by posterior pituitary gland
g. ADH antidiuretic hormone: negative feedback – restore blood’s normal osmotic conc = less & more conc urine
Detector: hypothalamus osmoreceptors – monitor blood solute potential + secrete ADH
o Dehydration: less water intake / sweating / high salt intake – more ADH
o Overhydration: excess water intake / low salt intake – less ADH
Coordinator: posterior pituitary gland – release ADH
Effector: permeability of distal convoluted tubule & collecting duct cell membranes to water – increases
o ADH binds to dct & cd membrane receptors
o triggers vesicles with aquaporins to fuse with membrane = inserted
o Aquaporins (intrinsic protein): contain pore allowing water to move out by osmosis
o Aquaporins removed when ADH concentration falls
- water reabsorbed → medulla tissue fluid → vasa recta (blood)
= blood water potential restored