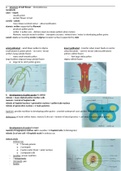
receptacle
calyx – sepals
- usually green
- protect flower in bud
corolla – petals
- may release scented nectar – attract pollinators
stamen: anther supported by filament
- produces pollen grains
- anther: 4 pollen sacs – dehisce (open & release pollen) when mature
- filament: vascular strand in anther – transports sucrose / mineral ions / water to developing pollen grains
carpel: ovary surrounding ovules & stigma (receptor surface) supported by style
wind pollinated – wind blows pollen to stigma insect pollinated – transfer when insect feeds on nectar
small/absent & green petals – no scent / nectar colourful petals – scent & nectar (attract pollinators)
anthers hang outside flower anthers within flower
- many small smooth pollen - few large sticky pollen
large feathery stigmas hang outside flower stigma within flower
o large SA to catch pollen grains
b. development of pollen grains in anther
mitosis = many diploid pollen mother cells
meiosis = tetrad of haploid cells
mitosis of haploid nucleus = generative nucleus + pollen tube nucleus
mitosis of generative nucleus = 2 male gametes
tapetum: provide nutrition to developing pollen grains – provide waterproof coat: protect from drying out (desiccation)
dehiscence of outer anther layers: mature & dry out = tension in lateral grooves = curl away = expose pollen grains
development of ovules in ovary
meiosis of megaspore mother cell in nucellus = 4 haploid cells (3 disintegrate)
mitosis 3x of one cell = 8 haploid nuclei in embryo sac
mature ovule
- embryo sac
o 1 female gamete
o 2 synergids
o 2 polar nuclei (fuse) = polar nucleus
o 3 antipodal cells
- nucellus: proves nutrition
- 2 integuments
- micropyle: gap
- funicle
, c. pollination: transfer of pollen from anther to stigma of same species
self-pollination same plant – self-fertilisation = inbreeding
- reduced genetic variation – relies on independent assortment & crossing over & mutation
- greater chance of 2 harmful recessive alleles coming together in fertilisation
+ preserve successful genomes – suited to environment
cross-pollination: another plant = outbreeding – combine gametes from 2 individuals
+ meiosis + mutation + cross-fertilisation = more genetic variation
+ reduced chance of harmful recessive alleles coming together
+ evolution for species to survive changing environment: genetic variation = more successful genomes
adaptations to ensure cross-pollination
- stamens & stigma ripen at different times
- stigma above anther: pollen can’t fall onto it
- chemical self-incompatibility: pollen can’t germinate on stigma of same plant
d. double fertilisation – 2 male gametes
- pollen grain germinates on stigma
- pollen tube nucleus controls pollen tube growth – codes for hydrolytic enzymes
enzymes digest path through style & ovary & micropyle (embryo sac) (products used for tube growth)
tube nucleus degenerates
1. fuses with female gamete = diploid zygote
2. fuses with polar nuclei = triploid primary endosperm nucleus
e. seed & fruit development – broad bean & maize
ovary = fruit
ovary wall = fruit wall – encloses seeds
ovule = seed
diploid zygote mitosis = diploid embryo
o plumule: developing shoot
o radicle: developing root
o 1-2 cotyledons: seed leaves
triploid endosperm nucleus mitosis = endosperm tissue – food store (nutrition) for developing embryo
integuments – dry / harden / waterproof / lignin depositions = testa (seed coat)
micropyle = pore in testa
funicle = funicle attached to seed at hilum
maize seeds: monocotyledon endosperm broad bean seeds: dicotyledon non-endosperms
endosperm remains (as food store) endosperm absorbed into cotyledons
testa & ovary wall fuse = 1-seeded fruit