TEFL 01.12.20
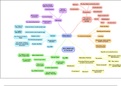
BICS: basic interpersonal communicative skills:
communicative conversational capacity which all learners acquire to communicate in different
situations
CALP: cognitiv/Academic language proficency:
CALP is said to occur in „context reduced“ academic situations. Where higher order thinking
skills /analysis, synthesis, evaluation) are recquired
communicative competence:
grammatic competence:
-vocabulary
-morphology
-syntax
-phonology
Textual competence:
mastering the linguistic code (on text level)
-cohesion
-rhetorical organization
illoctionary competence:
refers to ones abiliy to understand the message behind the words that one reads and hears,
social lingusitic functions:
– sensitivity to dialect or variety
– sensivity to register
– sensitivity to naturalness
functions of language
→ the purpose that we associate with a speech act
functions cannot be accomplished without forms of language
Speech acts:
-speaker makes an utterance to hearer in a context
-speaker performs action via utterance
→ youre fired
-part of social interactive behaviour
-interpreted as aspect
Speech event:
-circumstances, context surrounding the utterance
-determine the interpretation of an utterance
→ sometimes the speechact is indirect and an decryption is needed ( „its pretty cold in here“)
BICS: basic interpersonal communicative skills:
communicative conversational capacity which all learners acquire to communicate in different
situations
CALP: cognitiv/Academic language proficency:
CALP is said to occur in „context reduced“ academic situations. Where higher order thinking
skills /analysis, synthesis, evaluation) are recquired
communicative competence:
grammatic competence:
-vocabulary
-morphology
-syntax
-phonology
Textual competence:
mastering the linguistic code (on text level)
-cohesion
-rhetorical organization
illoctionary competence:
refers to ones abiliy to understand the message behind the words that one reads and hears,
social lingusitic functions:
– sensitivity to dialect or variety
– sensivity to register
– sensitivity to naturalness
functions of language
→ the purpose that we associate with a speech act
functions cannot be accomplished without forms of language
Speech acts:
-speaker makes an utterance to hearer in a context
-speaker performs action via utterance
→ youre fired
-part of social interactive behaviour
-interpreted as aspect
Speech event:
-circumstances, context surrounding the utterance
-determine the interpretation of an utterance
→ sometimes the speechact is indirect and an decryption is needed ( „its pretty cold in here“)