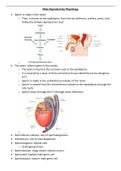
• Sperm is made in the testis
o Then, it moves to the epididymis, then the vas deferens, urethra, penis, and
finally the female reproductive tract
o
• The testis- where sperm is first made
o The testis is found in the scrotum next to the epididymis
o It is covered by a layer of thick connective tissue called the tunica albuginea
(CT)
o Sperm is made in the seminiferous tubules of the testis
o Sperm is moved from the seminiferous tubules to the epididymis through the
rete testis
o Sperm move through the CT through ducti efferentes
o
• Seminiferous tubules- site of spermatogenesis
• Interstitium- site of steroidogenesis
• Spermatogonia- diploid cells
o Undergoing miosis
• Spermatocyte- stage where meiosis occurs
• Spermatid- haploid male germ cell
• Spermatozoa- mature male germ cell
, •
• Germ cell maturation occurs from the basal to luminal surface of the seminiferous
epithelium
o
• Sertoli cells are the somatic supporting cells of spermatogenesis in the seminiferous
epithelium
o They span the entirety of the seminiferous epithelium
o Sertoli cells have many functions:
▪ Supportive- required to support developing germ cells
▪ Protective- form the blood-testis barrier which protects haploid germ
cells from the organism’s immune system
• Sperm may be recognised as foreign because the cells don’t have
the same genetics
▪ Secretory- secrete androgen binding protein into the lumen of the
tubule
▪ Hormonal- produce inhibins (suppresses FSH) and AMH
▪ Phagocytic- reabsorb products of sperm production that are released
from the seminiferous epithelia
▪ Spermatogenesis- help move spermatocytes from the basal membrane
to the lumen