DCL Task 2. Working memory
Learning goals:
- Development of working memory
- Explain Baddeley’s model
- When working memory does not develop properly and potential interventions
- Measuring WM, both behavioral and functional
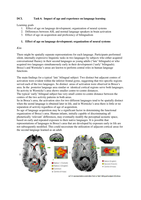
1. Working memory and its development
WM refers to a small amount of information that is most easily accessible to the conscious
mind at a given moment. The ability to understand a complex thought depends on how many
elements of thought can be kept in mind interrelated. STM only has basic storage properties.
Mental strategies and processes are used for problem solving. Working memory includes
STM but with the emphasis on the special role of focused attention. Includes control
processes that help to extend the time for which info can be kept in storage.
Several aspects of WM develop through childhood:
- Capacity
A chunk is a unit meaningful to the participant, and there is a limit as to how many one keep
in mind. Item capacity limits are a result of time limits, so WM is poorer for long words than
short ones. Limit of WM: 7 chunks, but when no rehearsal possible then only 3. Probably
because of focus of attention but can also be because similar sorts interfere with one another.
The number of associations between elements is restricted which limits the complexity of
thought. Older children: more slots/capacity than younger ones, and maybe more efficient
encoding can produce larger chunks. When remembering sentences: no difference between
how much of the sentence was accessed, but there was a difference in the number of sentences
accessed. So there is developmental growth in the number of slots in WM.
Developmental growth of WM could reflect the ability to concentrate on relevant items, but
research only shows this when there are too many items for the child so they become
overwhelmed and unable to concentrate on the more relevant items.
- Speed
Mnemonic processing increases in speed. This may account for developmental reductions in
memory loss or developmental increases in memory retention. Rapid processing is important
because it allows refreshment of the items to be remembered before their decay is complete.
So there is an increased rate of covert verbal rehearsal or increased rate of attentional
refreshing. There is a linear line between the number of items one can recall in 2 seconds and
recital rate. Older children can recall more and recite faster. Children younger than 4y do not
seem to use attention to refresh items. For them, the limit in performance depends on the
duration of the retention interval. For older children and adults, who are able to refresh, it is
not the absolute duration but the cognitive load that determines performance. Attention must
be switched between tasks in complex span to protect from decay, an more mature
participants do this better; attentional refreshing is slower in young children. Increase in speed
is linked to increase in capacity as well.
- Knowledge
Increasing knowledge is also important for remembering; if one knows more about the things
they have to remember: bootstrapping. familiarity with the materials determines the
processing speed, which in turn determines the span.
- Use of strategies
Learning goals:
- Development of working memory
- Explain Baddeley’s model
- When working memory does not develop properly and potential interventions
- Measuring WM, both behavioral and functional
1. Working memory and its development
WM refers to a small amount of information that is most easily accessible to the conscious
mind at a given moment. The ability to understand a complex thought depends on how many
elements of thought can be kept in mind interrelated. STM only has basic storage properties.
Mental strategies and processes are used for problem solving. Working memory includes
STM but with the emphasis on the special role of focused attention. Includes control
processes that help to extend the time for which info can be kept in storage.
Several aspects of WM develop through childhood:
- Capacity
A chunk is a unit meaningful to the participant, and there is a limit as to how many one keep
in mind. Item capacity limits are a result of time limits, so WM is poorer for long words than
short ones. Limit of WM: 7 chunks, but when no rehearsal possible then only 3. Probably
because of focus of attention but can also be because similar sorts interfere with one another.
The number of associations between elements is restricted which limits the complexity of
thought. Older children: more slots/capacity than younger ones, and maybe more efficient
encoding can produce larger chunks. When remembering sentences: no difference between
how much of the sentence was accessed, but there was a difference in the number of sentences
accessed. So there is developmental growth in the number of slots in WM.
Developmental growth of WM could reflect the ability to concentrate on relevant items, but
research only shows this when there are too many items for the child so they become
overwhelmed and unable to concentrate on the more relevant items.
- Speed
Mnemonic processing increases in speed. This may account for developmental reductions in
memory loss or developmental increases in memory retention. Rapid processing is important
because it allows refreshment of the items to be remembered before their decay is complete.
So there is an increased rate of covert verbal rehearsal or increased rate of attentional
refreshing. There is a linear line between the number of items one can recall in 2 seconds and
recital rate. Older children can recall more and recite faster. Children younger than 4y do not
seem to use attention to refresh items. For them, the limit in performance depends on the
duration of the retention interval. For older children and adults, who are able to refresh, it is
not the absolute duration but the cognitive load that determines performance. Attention must
be switched between tasks in complex span to protect from decay, an more mature
participants do this better; attentional refreshing is slower in young children. Increase in speed
is linked to increase in capacity as well.
- Knowledge
Increasing knowledge is also important for remembering; if one knows more about the things
they have to remember: bootstrapping. familiarity with the materials determines the
processing speed, which in turn determines the span.
- Use of strategies