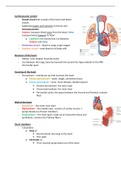
Cardiovascular system
- Closed circuit that consists of the heart and blood
vessels
- Supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues and
removing wastes
- Arteries transport blood away from the heart; Veins
transport blood towards to heart
o Capillaries are vessels that run between
Arteries and Veins
- Pulmonary circuit – blood to lungs to get oxygen
- Systemic circuit – send blood to all body cells
Structure of the heart
- Hollow, cone shaped, muscular pump
- Lies between the lungs, base lies beneath the second rib; Apex extends to the fifth
intercostal space
Covering of the heart
- Pericardium – membrane sac that encloses the heart
o Fibrous pericardium – outer, tough, connective tissue
o Serous pericardium – inner, more delicate, double-layered
Parietal pericardium: the outer layer
Visceral pericardium: the inner layer
Pericardial cavity: the space between the Visceral and Parietal; contains
fluid
Wall of the heart
- Epicardium – the outer most layer
- Myocardium – the middle layer, consists of cardiac muscle ->
pumps blood out of heart chambers
- Endocardium – the inner layer, made up of connective tissue and
epithelium, contains the Purkinje fibers
Heart chambers
- 4 chambers
o Atria x2
Receive blood returning to the heart
Thin walls
o Ventricles x2
Thick muscled pump blood out of the heart
, - Each side has an atrioventricular valve
o Right tricuspid valve
o Left bicuspid or mitral valve
o Valve are attached to papillary muscles in the inner wall of the heart
Skeleton of the heart
- Rings of dense connective tissue
- Provide attachment for the heart valves and muscle fibers
- Skeleton of the heart = fibrous rings + dense connective tissues interventricular septum
Blood flow through the heart
- Pulmonary circuit – blood flow between heart and lungs
- Systemic circuit – Blood flow between heart and body tissues
- Closed circuit that consists of the heart and blood
vessels
- Supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues and
removing wastes
- Arteries transport blood away from the heart; Veins
transport blood towards to heart
o Capillaries are vessels that run between
Arteries and Veins
- Pulmonary circuit – blood to lungs to get oxygen
- Systemic circuit – send blood to all body cells
Structure of the heart
- Hollow, cone shaped, muscular pump
- Lies between the lungs, base lies beneath the second rib; Apex extends to the fifth
intercostal space
Covering of the heart
- Pericardium – membrane sac that encloses the heart
o Fibrous pericardium – outer, tough, connective tissue
o Serous pericardium – inner, more delicate, double-layered
Parietal pericardium: the outer layer
Visceral pericardium: the inner layer
Pericardial cavity: the space between the Visceral and Parietal; contains
fluid
Wall of the heart
- Epicardium – the outer most layer
- Myocardium – the middle layer, consists of cardiac muscle ->
pumps blood out of heart chambers
- Endocardium – the inner layer, made up of connective tissue and
epithelium, contains the Purkinje fibers
Heart chambers
- 4 chambers
o Atria x2
Receive blood returning to the heart
Thin walls
o Ventricles x2
Thick muscled pump blood out of the heart
, - Each side has an atrioventricular valve
o Right tricuspid valve
o Left bicuspid or mitral valve
o Valve are attached to papillary muscles in the inner wall of the heart
Skeleton of the heart
- Rings of dense connective tissue
- Provide attachment for the heart valves and muscle fibers
- Skeleton of the heart = fibrous rings + dense connective tissues interventricular septum
Blood flow through the heart
- Pulmonary circuit – blood flow between heart and lungs
- Systemic circuit – Blood flow between heart and body tissues