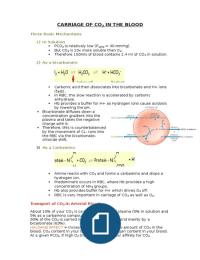
CARRIAGE OF CO2 IN THE BLOOD
Three Basic Mechanisms
1) In Solution
PCO2 is relatively low (PaCO2 = 40 mmHg).
But CO2 is 20x more soluble than O2.
Therefore 100mls of blood contains 2.4 ml of CO 2 in solution.
2) As a bicarbonate
Carbonic acid then dissociates into bicarbonate and H+ ions
(fast).
In RBC, the slow reaction is accelerated by carbonic
anhydrase.
Hb provides a buffer for H+ as Hydrogen ions cause acidosis
by lowering the pH.
Bicarbonate diffuses down a
concentration gradient into the
plasma and takes the negative
charge with it.
Therefore, this is counterbalanced
by the movement of CL- ions into
the RBC via the bicarbonate-
chloride shift.
3) As a Carbamino
Amine reacts with CO2 and forms a carbamino and drops a
hydrogen ion.
Predominant occurs in RBC, where Hb provides a high
concentration of NH2 groups.
Hb also provides buffer for H+ which drives O 2 off.
RBC is very important in carriage of CO2 as well as O2.
Transport of CO2 in Arterial Blood
About 10% of your CO2 is carried in your blood plasma (5% in solution and
5% as a carbamino compound).
90% of the CO2 is carried in your red blood cells and mainly by a
bicarbonate (63%).
HALDANE EFFECT = Increasing PO2 decreases the amount of CO2 in the
blood. CO2 content in your blood is 2.5x the oxygen content in your blood.
At a given PCO2, if high O2 then you have a lower affinity for CO2.
Three Basic Mechanisms
1) In Solution
PCO2 is relatively low (PaCO2 = 40 mmHg).
But CO2 is 20x more soluble than O2.
Therefore 100mls of blood contains 2.4 ml of CO 2 in solution.
2) As a bicarbonate
Carbonic acid then dissociates into bicarbonate and H+ ions
(fast).
In RBC, the slow reaction is accelerated by carbonic
anhydrase.
Hb provides a buffer for H+ as Hydrogen ions cause acidosis
by lowering the pH.
Bicarbonate diffuses down a
concentration gradient into the
plasma and takes the negative
charge with it.
Therefore, this is counterbalanced
by the movement of CL- ions into
the RBC via the bicarbonate-
chloride shift.
3) As a Carbamino
Amine reacts with CO2 and forms a carbamino and drops a
hydrogen ion.
Predominant occurs in RBC, where Hb provides a high
concentration of NH2 groups.
Hb also provides buffer for H+ which drives O 2 off.
RBC is very important in carriage of CO2 as well as O2.
Transport of CO2 in Arterial Blood
About 10% of your CO2 is carried in your blood plasma (5% in solution and
5% as a carbamino compound).
90% of the CO2 is carried in your red blood cells and mainly by a
bicarbonate (63%).
HALDANE EFFECT = Increasing PO2 decreases the amount of CO2 in the
blood. CO2 content in your blood is 2.5x the oxygen content in your blood.
At a given PCO2, if high O2 then you have a lower affinity for CO2.