Module 5: Physical chemistry and transition elements
Table of Content
5.1 Rates, equilibrium and pH ................................................. 2
5.1.1 How fast? .................................................................................................................... 2
Rate-determining step ...................................................................................................... 4
Effect of temp on rate constant........................................................................................ 6
5.1.2 How far? ..................................................................................................................... 7
Equilibrium constant, Kc ................................................................................................... 7
Gaseous Equilibria, Kp .................................................................................................... 10
5.1.3 Acids, bases and buffers ........................................................................................... 14
Brønsted–Lowry acids and bases .................................................................................... 14
pH, Ka, Kw ....................................................................................................................... 15
Buffers ............................................................................................................................ 16
Neutralisation - pH titration curves ................................................................................ 17
2.2 Energy ............................................................................. 18
5.2.1 Lattice enthalpy, ΔLEH⦵ ............................................................................................ 18
5.2.2 Enthalpy and entropy ............................................................................................... 21
5.2.3 Redox and electrode potentials ............................................................................... 23
Redox titration with half equations ................................................................................ 23
Electrode potentials........................................................................................................ 24
5.3 Transition elements ........................................................ 26
5.3.1 Transition elements.................................................................................................. 26
Transition elements properties ...................................................................................... 26
Ligands and complex ions ............................................................................................... 27
Precipitation reactions.................................................................................................... 30
Redox reactions .............................................................................................................. 31
5.3.2 Qualitative analysis .................................................................................................. 32
1
, OCR A level Chemistry notes Module 5: Physical chemistry and transition elements
5.1 Rates, equilibrium and pH
5.1.1 How fast?
Rate of reaction
𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 (𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑑𝑚!" )
𝑅𝑎𝑡𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 = = 𝑔𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑡
𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 (𝑠)
Initial rate: rate at t = 0
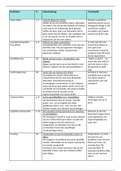
Suggest why initial rates of reaction are used to determine these orders rather than rates of reaction at
other times during the experiment (1)
• (At start) the concentrations are known
Start how the initial rate is obtained from a graph of the concentration of the product against time (2)
• (Calculate) gradient (of tangent) at t=0
Rate equation
Rate constant
• Constant of proportionality between rate and conc. of reactant
• Only temp affects rate constant
o ↑ temp ↑ rate constant
What happens to the rate constant if ↑ pressure? (1)
• No change
Order: the power to which the conc. of a reactant is raised to
Overall order: sum of all orders in the rate equation m + n
Order of reaction: rate ∝ [A]n
Zero order First order Second order
• rate ∝ [A]0 • rate ∝ [A]1 • rate ∝ [A]2
• Has no effect on the rate • If [A] × 2 ⇒ reaction rate × 2 • If [A] × 3 ⇒ reaction
• Constant negative gradient (21 = 2) rate × 9 (32 = 9)
in conc-time graph • Concentration of half-lives is
constant in conc-time graph
• Straight diagonal line via
(0,0) in rate-conc graph
2
, OCR A level Chemistry notes Module 5: Physical chemistry and transition elements
Concentration-time graph Rate-concentration graph
1st order reactions & half life (t1/2)
• Time for [reactant] is constant
𝐼𝑛2
𝑘=
𝑡#/%
Suggest how conc of bromine can be monitored? (1)
• Measure reduction of colour of bromine
Suggest a different experimental method to allow reactant rates to be followed overtime (1)
• Measure volume of CO2 produced
3
, OCR A level Chemistry notes Module 5: Physical chemistry and transition elements
Rate-determining step
Rate-determining step (RDS): slowest step in a multistep reaction mechanism
• Steps in a multi-step reaction take place at a different rate
• Rate equation only includes reacting species involved in RDS
• Orders in rate equation match no. of species involved in RDS
Suggest a reaction mechanism for this reaction
(CH3)3CBr + OH- → (CH3)3COH + Br-
Rate equation: rate = k[(CH3)3CBr]
• Step 1: (CH3)3CBr → (CH3)3C+ + Br- Slow (RDS)
• Step 2: (CH3)3C+ + OH- → (CH3)3COH Fast
4