INTRODUCTION TO RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY:
LUNG VOLUMES
Respiration = oxygen delivered to cells of body and enables them
to produce energy by oxidative reactions and by-product is CO2
release.
External respiration = breathing in/out of lungs
Internal Respiration = exchange of gas between tissue and blood.
Cellular respiration = chemical reactions within cell that use O 2 to produce
energy.
Pharynx-Larynx-Trachea-Bronchi-Bronchioles-Alveoli
As air is breathed in, gas is warmed/humidified by the walls of the airways
close to body temperature whilst passing through the lungs so it doesn’t
damage the alveolar membranes.
Protection mechanisms of the lungs from foreign invasive matter:
1. Nose has fine hairs to filter particles
2. Bronchi are coated with mucus so matter is trapped
3. Macrophages in alveoli to engulf foreign matter.
Dead Space – volume of gas within the lungs that doesn’t take part in gas
exchange.
Total CS area increases down the airways as diameter decreases.
Trachea
Supporting cartilage (alongside
bronchi) to prevent collapse
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar
epithelium.
Goblet cells produce mucin (mucus
precursor)
Mucocilary escalator - Cilia push
mucus up airways and attract foreign
matter which is coughed up.
Bronchioles
Lack cartilage; patency maintained by
connective tissue (lung parenchyma) by
radial traction.
Diameter <1mm
Cuboidal epithelium
Smooth muscle in walls
Large amount of alveolar wall is taken up by
capillaries; therefore, increasing SA for gas exchange.
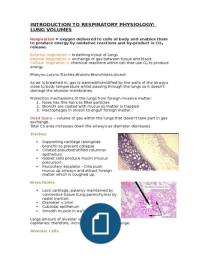
Alveolar Cells
LUNG VOLUMES
Respiration = oxygen delivered to cells of body and enables them
to produce energy by oxidative reactions and by-product is CO2
release.
External respiration = breathing in/out of lungs
Internal Respiration = exchange of gas between tissue and blood.
Cellular respiration = chemical reactions within cell that use O 2 to produce
energy.
Pharynx-Larynx-Trachea-Bronchi-Bronchioles-Alveoli
As air is breathed in, gas is warmed/humidified by the walls of the airways
close to body temperature whilst passing through the lungs so it doesn’t
damage the alveolar membranes.
Protection mechanisms of the lungs from foreign invasive matter:
1. Nose has fine hairs to filter particles
2. Bronchi are coated with mucus so matter is trapped
3. Macrophages in alveoli to engulf foreign matter.
Dead Space – volume of gas within the lungs that doesn’t take part in gas
exchange.
Total CS area increases down the airways as diameter decreases.
Trachea
Supporting cartilage (alongside
bronchi) to prevent collapse
Ciliated pseudostratified columnar
epithelium.
Goblet cells produce mucin (mucus
precursor)
Mucocilary escalator - Cilia push
mucus up airways and attract foreign
matter which is coughed up.
Bronchioles
Lack cartilage; patency maintained by
connective tissue (lung parenchyma) by
radial traction.
Diameter <1mm
Cuboidal epithelium
Smooth muscle in walls
Large amount of alveolar wall is taken up by
capillaries; therefore, increasing SA for gas exchange.
Alveolar Cells