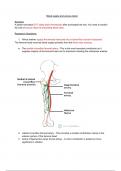
Introduction to Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology
o The study of how people perceive, learn, remember, think about information
Cognitive psychologist
o Study how people perceive various shapes, why they remember some facts but forget
others, or how they learn language
Progression of ideas involves:
Dialectic – a developmental process whereby ideas evolve over time through a pattern of
transformation
Patterns of transformation:
• Thesis (statement of belief) is proposed (e.g. human nature governs many aspects of
human behavior such as intelligence or personality)
• Antithesis (statement that counters previous beliefs) emerges (e.g. nurture determines
many aspects of human behavior)
• Synthesis – integrates the most credible features of thesis and antithesis (e.g. the
interaction between our innate nature and environmental nurture may govern human
behavior)
Philosophical antecedents of psychology
• Philosophy
o understand the general nature of the many aspects of the world
o introspection
o intro – “inward, within”
o spec – “look”
• Physiology
o Seeks a scientific study of life-sustaining functions in living matter
o Through empirical (observation-based) methods
Approaches to the study of the mind
Cognitive psychology
o The study of how people perceive, learn, remember, think about information
Cognitive psychologist
o Study how people perceive various shapes, why they remember some facts but forget
others, or how they learn language
Progression of ideas involves:
Dialectic – a developmental process whereby ideas evolve over time through a pattern of
transformation
Patterns of transformation:
• Thesis (statement of belief) is proposed (e.g. human nature governs many aspects of
human behavior such as intelligence or personality)
• Antithesis (statement that counters previous beliefs) emerges (e.g. nurture determines
many aspects of human behavior)
• Synthesis – integrates the most credible features of thesis and antithesis (e.g. the
interaction between our innate nature and environmental nurture may govern human
behavior)
Philosophical antecedents of psychology
• Philosophy
o understand the general nature of the many aspects of the world
o introspection
o intro – “inward, within”
o spec – “look”
• Physiology
o Seeks a scientific study of life-sustaining functions in living matter
o Through empirical (observation-based) methods
Approaches to the study of the mind