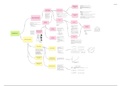
- Rank the criteria in the order of the decision maker's
preference
- Steps:
Ranking Method - Straight ranking (the most important =1, 2nd
important =2 etc)
- Estimation of the k-th criterion weight :
s
de
clu
In
- Decision makers estimate weights on the basis of a
predetermined scale; for example, a
Rating Method scale of 0 to 100
Global Criteria es - Given the scale, a score of 100 is assigned to the most
Includ important criterion.
Weighting - Proportionately smaller weights are then given to
criteria lower in the order.
- The procedure is continued until a score is assigned
Value Scaling to the least important criterion
(Part 1)* - Finally, the weights are normalized by dividing each
In
of the weights by the sum total
clu
de
Includes
s
Pairwise Approximating the
comparison Includes values of criterion
Includ
weights
es
Criterion Weighting - Employs an underlying scale with values from 1 to 9 to
Includes
Inc rate the preferences with respect to a pair of criteria
lud Local Criteria - Pairwise comparisons are organized into a matrix:
es
Weighting
- Unlike the ranking, rating, and pairwise comparison
- Weight: a value assigned to an evaluation Entropy-Based methods, the entropy-based criterion weighting
criterion that indicates its importance relative to
Includes
approach does not require the decision making agents
the other criteria under consideration Criterion Weights to specify their preferences with respect to the
- Weighting methods can be classified into two evaluation criteria
categories of: - Entropy-Based Criterion Weights method is based on
- Global methods the concept of information entropy.
- Based on the assumption of spatial - Entropy: a measure of the expected information
homogeneity of preferences content of a massage
- Local Methods Includes
- Taking into account spatial - The entropy-based criterion weights can be combined
heterogeneity of preferences with weights obtained using one of the other
GIS-MCDA Part 2 methods discussed:
Criterion weights, should
- Adjusting preferences according to the spatial
follow:
relationship between alternatives
Multi-attribute and -Multicriteria design rules can be broadly - The values of the entropy-based criterion weights:
- This method explicitly acknowledges the concept of
- Weights must be ratio scaled: categorized into two groups: and range from 0 to 1
- If criterion C1 is twice as 'important' as Multi-Objective - Multi-attribute decision analysis (MADA)
spatial heterogeneity of preferences
- Proximity-adjusted criterion weights by introducing a
C2, then w1 =2w2, that is w1 = 0.667 and Methods - Involve a predetermined, limited
reference or benchmark location
w2=0.333 number of alternatives
- Multi-objective decision analysis (MODA)
Includes
- The weights should reflect both:
- Process-oriented design and search
- Relative importance of the criterion
- Make a distinction between the concept
Proximity-Adjusted - Assessed in terms of the global criterion weight
des
of decision variables and decision criteria
- Spatial position of a decision alternative with respect to
Criterion Weights
Inclu
a reference location
- Assessed in terms of a distance decay function:
the closer a given alternative is situated to a reference
location, the higher the value of the criterion weight
should be
Combination Rules
Range-Based Local
Criterion Weights
- Combination rule (decision rule) integrates the data and
Includes
information about alternatives (criterion maps) and
decision maker’s preferences (criterion weights) into an
overall assessment of the alternatives
Compensatory
- Decision rules can be classified into four groups of: - Allow-trade-off a low value on one criterion
- Compensatory versus non-compensatory against a high value on another
- Multi-attribute versus multi-objective - Example: weighted linear combination
- Discrete versus continues methods
- Spatially implicit versus spatially explicit MCDA Non-compensatory
Compensatory vs - Boolean overlay operations in the form of:
Non-compensatory
s
- Conjunctive screening methods
Entropy-Based Local
Include
- An alternative is accepted if it meets
specified standards or thresholds for all evaluation Criterion Weights
criteria
- Disjunctive screening methods
- Accepts alternative scores sufficiently
high on at least one of the criteria under
consideration
- Overlaps with the multi-attribute/ multi-objective dichotomy
Discrete and - Example: Site Selection (discrete) versus site search (continuous) problems
Continuous
- Site Selection: identify the best site for some activity given the set of potential Site Selection VS
(feasible) sites
s Site Search
Methods - All the characteristics (such as location, size, and relevant attributes) of the Include
candidate sites are known
- The problem is to rate or rank the alternative sites based on their characteristics
so that the best site (or a set of sites) can be identified
- Site Search Analysis: No pre-determined set of candidate sites
- The characteristics of the sites (i.e., their boundaries) have to be defined by
solving the problem
- The aim of the site search analysis is to explicitly identify the boundary of the
best site(s)
preference
- Steps:
Ranking Method - Straight ranking (the most important =1, 2nd
important =2 etc)
- Estimation of the k-th criterion weight :
s
de
clu
In
- Decision makers estimate weights on the basis of a
predetermined scale; for example, a
Rating Method scale of 0 to 100
Global Criteria es - Given the scale, a score of 100 is assigned to the most
Includ important criterion.
Weighting - Proportionately smaller weights are then given to
criteria lower in the order.
- The procedure is continued until a score is assigned
Value Scaling to the least important criterion
(Part 1)* - Finally, the weights are normalized by dividing each
In
of the weights by the sum total
clu
de
Includes
s
Pairwise Approximating the
comparison Includes values of criterion
Includ
weights
es
Criterion Weighting - Employs an underlying scale with values from 1 to 9 to
Includes
Inc rate the preferences with respect to a pair of criteria
lud Local Criteria - Pairwise comparisons are organized into a matrix:
es
Weighting
- Unlike the ranking, rating, and pairwise comparison
- Weight: a value assigned to an evaluation Entropy-Based methods, the entropy-based criterion weighting
criterion that indicates its importance relative to
Includes
approach does not require the decision making agents
the other criteria under consideration Criterion Weights to specify their preferences with respect to the
- Weighting methods can be classified into two evaluation criteria
categories of: - Entropy-Based Criterion Weights method is based on
- Global methods the concept of information entropy.
- Based on the assumption of spatial - Entropy: a measure of the expected information
homogeneity of preferences content of a massage
- Local Methods Includes
- Taking into account spatial - The entropy-based criterion weights can be combined
heterogeneity of preferences with weights obtained using one of the other
GIS-MCDA Part 2 methods discussed:
Criterion weights, should
- Adjusting preferences according to the spatial
follow:
relationship between alternatives
Multi-attribute and -Multicriteria design rules can be broadly - The values of the entropy-based criterion weights:
- This method explicitly acknowledges the concept of
- Weights must be ratio scaled: categorized into two groups: and range from 0 to 1
- If criterion C1 is twice as 'important' as Multi-Objective - Multi-attribute decision analysis (MADA)
spatial heterogeneity of preferences
- Proximity-adjusted criterion weights by introducing a
C2, then w1 =2w2, that is w1 = 0.667 and Methods - Involve a predetermined, limited
reference or benchmark location
w2=0.333 number of alternatives
- Multi-objective decision analysis (MODA)
Includes
- The weights should reflect both:
- Process-oriented design and search
- Relative importance of the criterion
- Make a distinction between the concept
Proximity-Adjusted - Assessed in terms of the global criterion weight
des
of decision variables and decision criteria
- Spatial position of a decision alternative with respect to
Criterion Weights
Inclu
a reference location
- Assessed in terms of a distance decay function:
the closer a given alternative is situated to a reference
location, the higher the value of the criterion weight
should be
Combination Rules
Range-Based Local
Criterion Weights
- Combination rule (decision rule) integrates the data and
Includes
information about alternatives (criterion maps) and
decision maker’s preferences (criterion weights) into an
overall assessment of the alternatives
Compensatory
- Decision rules can be classified into four groups of: - Allow-trade-off a low value on one criterion
- Compensatory versus non-compensatory against a high value on another
- Multi-attribute versus multi-objective - Example: weighted linear combination
- Discrete versus continues methods
- Spatially implicit versus spatially explicit MCDA Non-compensatory
Compensatory vs - Boolean overlay operations in the form of:
Non-compensatory
s
- Conjunctive screening methods
Entropy-Based Local
Include
- An alternative is accepted if it meets
specified standards or thresholds for all evaluation Criterion Weights
criteria
- Disjunctive screening methods
- Accepts alternative scores sufficiently
high on at least one of the criteria under
consideration
- Overlaps with the multi-attribute/ multi-objective dichotomy
Discrete and - Example: Site Selection (discrete) versus site search (continuous) problems
Continuous
- Site Selection: identify the best site for some activity given the set of potential Site Selection VS
(feasible) sites
s Site Search
Methods - All the characteristics (such as location, size, and relevant attributes) of the Include
candidate sites are known
- The problem is to rate or rank the alternative sites based on their characteristics
so that the best site (or a set of sites) can be identified
- Site Search Analysis: No pre-determined set of candidate sites
- The characteristics of the sites (i.e., their boundaries) have to be defined by
solving the problem
- The aim of the site search analysis is to explicitly identify the boundary of the
best site(s)