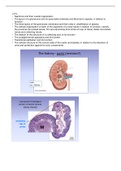
• Nephrons and their overall organization
• The layout of a glomerulus and its associated arterioles and Bowman’s capsule, in relation to
function
• The three layers of the glomerular membrane and their roles in ultra ltration of plasma
• The cellular organization of each of the segments of a renal tubule in relation to function, namely
the proximal convoluted tubule, thin and ascending thick limbs of loop of Henle, distal convoluted
tubule and collecting tubule
• The relation of the structure of a collecting duct to its function
• The juxtaglomerular apparatus and its function
• Transitional epithelium and its function
• The cellular structure of the normal walls of the ureter and bladder, in relation to the retention of
urine and protection against its toxic components
, renal corpuscle
the glomerulus
• knot of capillaries
• SEM image
• has a lter formed by specialised e.cells coating capillaries:
PODOCYTES - 'podo' - foot like
• podocytes have branches that have further brances = 'feet'
3 stages of ltration
A. FENESTRATION - gaps between e.cells that line wall of capillary
a. between capillary e.cell of glomerulus
B. BASEMENT MEMBRANES - ner sieve (THICK)
a. allows movement of small molecules and screens out big ones
C. FILTRATION SLIT MEMBRANE - outside surrounding the capillaries
a. small nanometre size - BETWEEN PODOCYTE FOOT PROCESSES (4nm pores)
• ltration occurs BOTH SIDES + ALL THE WAY AROUND THE CAPILLARY
proximal convoluted tubule
• REABSORPTION form ultra ltrate
• PASSIVE FLUX - small molecules with a conc gradient can pass through and return to blood
supply eg H2O, Cl- ions
• ACTIVE TRANSPORT - against conv gradient for eg glucose, amino acids, Na+ ions
• PINOCYTOSIS - for transport of macromolecules and larger proteins
◦ taken in e.cells via pinocytosis
◦ type of ENDOCYTOSIS (membrane engulfs molecules that fuse with lysosome)
◦ liberate consituent amino acids that are recycled in the blood
• microvilli = HIGH SA - lytic enzymes on surface to break down
macromolecules
• pinocytotic vesicles - CARRIES MACROMOLECULES -->
LYSOSOMES
• lysosomes
• mitochondria - FUELS active transport
LOOP OF HENLE (thin arm)
• REABSORPTION from ultra ltrate
• by passive ux (osmosis)
• THIN LOOP - squamous e.cell to
allow passive ux
• minimum of organelles
• thin to facilitate di usion
• move downwards
•