International law
Week 6
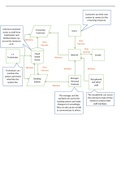
1. Concept of international law:
Concept: Body of rules and principles that regulates the conduct and relations of States 1 and
international organizations (and sometimes individuals but only if it refers to human rights).
- International law takes a bit of the state´s sovereignty (this is done by the state
voluntarily).
Public international law has 2 fields: traditional field and modern field.
2. Characteristics of international law (and its differences to domestic law):
- No international legislative body (international law is made from treaty and
customary law).
- No body able to enforce rules
- No court of compulsory jurisdiction (Ex: states need to accept jurisdiction of ICJ for it
to be binding)
3. Reasons to have international law:
- Need for states ‘coexistence to maintain peace and security.
4. Reasons why international law is respected
- Retro alimentary system (as it maintains itself): If state X attacks state Y, then the
latter one could simply attack any other state.
- State´s interest to respect international law= to ensure that a state is not alienated by
the others
- UN Security Council can implement sanctions or even use military action against a
state.
5. Subjects of international law:
a. States: Considered a state if it has a. defined territory, b. permanent population, c.
government that can execute effective authority (d. recognition by other states).
b. International organizations (IGO´s): either intergovernmental organization2 or
supranational organization3.
c. Individuals: They have rights (human rights Ex: ICCR (International convention of
children´s rights which is signed by almost all states except for the U.S) and
1
2
No transfer of sovereignty, decisions by unanimity (only binding if everyone agrees) Ex: UN
3
Trasnfer of sovereignty, decisions by majority (binding no matter if minority disagrees) Ex: EU, UN Security
Council
Week 6
1. Concept of international law:
Concept: Body of rules and principles that regulates the conduct and relations of States 1 and
international organizations (and sometimes individuals but only if it refers to human rights).
- International law takes a bit of the state´s sovereignty (this is done by the state
voluntarily).
Public international law has 2 fields: traditional field and modern field.
2. Characteristics of international law (and its differences to domestic law):
- No international legislative body (international law is made from treaty and
customary law).
- No body able to enforce rules
- No court of compulsory jurisdiction (Ex: states need to accept jurisdiction of ICJ for it
to be binding)
3. Reasons to have international law:
- Need for states ‘coexistence to maintain peace and security.
4. Reasons why international law is respected
- Retro alimentary system (as it maintains itself): If state X attacks state Y, then the
latter one could simply attack any other state.
- State´s interest to respect international law= to ensure that a state is not alienated by
the others
- UN Security Council can implement sanctions or even use military action against a
state.
5. Subjects of international law:
a. States: Considered a state if it has a. defined territory, b. permanent population, c.
government that can execute effective authority (d. recognition by other states).
b. International organizations (IGO´s): either intergovernmental organization2 or
supranational organization3.
c. Individuals: They have rights (human rights Ex: ICCR (International convention of
children´s rights which is signed by almost all states except for the U.S) and
1
2
No transfer of sovereignty, decisions by unanimity (only binding if everyone agrees) Ex: UN
3
Trasnfer of sovereignty, decisions by majority (binding no matter if minority disagrees) Ex: EU, UN Security
Council