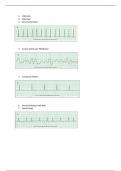
Sequencing → comparing the normal DNA with the tumour DNA with labelled nucleotides.
When you see double waves at such a sequencing graph, it is a frameshift, because you’ll have a
wildtype version and a mutated version. (Slide with: deletion of G).
Massive Parallel Sequencing or Next Generation Sequencing
➢ High throughput sequencing method of whole genomes
➢ Allows detection of mutations, chromosomal changes and translocations
c.384A>T c. = RNA sequence, 384 = the number of the nucleotide
g.16000A>T g. means genomic sequence.
p.Gly85>Glu p. is a protein
ATG = Start codon. A is the 1st nucleotide (number 1). Here you start counting. 5’ of RNA is capped
and the 3’end has PolyA.
Epigenetic changes are modifications. CpG → CmpG. It can induce gene silencing. In cancer: hypo-
and hypermethylation in tumor suppressor genes (TSGs). Bisulfite modifications cause the formation
of uracil instead of Cytosine → detect methylated C’s since they stay the same.
Lecture 4 The Cell Cycle
Rob Wolthuis
S-phase: DNA replication fork (replisome) consists of multiple DNA polymerases incorporated in a
molecular machine containing helicases and ligases and topo-isomerases. Leading and lagging strand.
Risk: fork collapse and DNA replication stress (nucleotide depletion, DNA damage, slowing down).
The duplicated chromosome is still connected with the previous chromosome (X shape during
replication → connection = kinetochore). Microtubules (mitotic spindle) connect to these
kinetochores of the chromatids during mitosis.
Cell division usually takes about one day. G1 = 11h, S = 6h, G2 = 6h, Mitosis = 40min.
1. Keep the Replicated Chromosomes Together
2. Condense the DNA
3. Remove the Nuclear Membrane
4. Build a Mechanical Structure: the Mitotic Spindle
5. Properly Attach All the Chromosomes to the Spindle
6. Separate the Sister Chromatids and Pull them apart
7. Make New Nuclei and Decondense the DNA
S = Synthesis of sister chromatids. G2 = sister chromatids condense but remain joint. Mitosis is a
dangerous state, therefore it doesn’t take long. The cells don’t have a nucleus at this point. The
chromosomes are floating through the cell.
Prophase = condensing phase. Prometaphase = trying to get the chromosomes in the middle.
Eventually (after mitosis) you’ll have two diploid cells (daughter cells).
Cyclin B1 bound to Cdk1 (cyclin dependant kinase) induces mitosis. First: appearance of cyclin B, then
activation of cyclin B (mitosis). When Cyclin B1 disappears → mitosis stops and G1 phase is induced.
When you see double waves at such a sequencing graph, it is a frameshift, because you’ll have a
wildtype version and a mutated version. (Slide with: deletion of G).
Massive Parallel Sequencing or Next Generation Sequencing
➢ High throughput sequencing method of whole genomes
➢ Allows detection of mutations, chromosomal changes and translocations
c.384A>T c. = RNA sequence, 384 = the number of the nucleotide
g.16000A>T g. means genomic sequence.
p.Gly85>Glu p. is a protein
ATG = Start codon. A is the 1st nucleotide (number 1). Here you start counting. 5’ of RNA is capped
and the 3’end has PolyA.
Epigenetic changes are modifications. CpG → CmpG. It can induce gene silencing. In cancer: hypo-
and hypermethylation in tumor suppressor genes (TSGs). Bisulfite modifications cause the formation
of uracil instead of Cytosine → detect methylated C’s since they stay the same.
Lecture 4 The Cell Cycle
Rob Wolthuis
S-phase: DNA replication fork (replisome) consists of multiple DNA polymerases incorporated in a
molecular machine containing helicases and ligases and topo-isomerases. Leading and lagging strand.
Risk: fork collapse and DNA replication stress (nucleotide depletion, DNA damage, slowing down).
The duplicated chromosome is still connected with the previous chromosome (X shape during
replication → connection = kinetochore). Microtubules (mitotic spindle) connect to these
kinetochores of the chromatids during mitosis.
Cell division usually takes about one day. G1 = 11h, S = 6h, G2 = 6h, Mitosis = 40min.
1. Keep the Replicated Chromosomes Together
2. Condense the DNA
3. Remove the Nuclear Membrane
4. Build a Mechanical Structure: the Mitotic Spindle
5. Properly Attach All the Chromosomes to the Spindle
6. Separate the Sister Chromatids and Pull them apart
7. Make New Nuclei and Decondense the DNA
S = Synthesis of sister chromatids. G2 = sister chromatids condense but remain joint. Mitosis is a
dangerous state, therefore it doesn’t take long. The cells don’t have a nucleus at this point. The
chromosomes are floating through the cell.
Prophase = condensing phase. Prometaphase = trying to get the chromosomes in the middle.
Eventually (after mitosis) you’ll have two diploid cells (daughter cells).
Cyclin B1 bound to Cdk1 (cyclin dependant kinase) induces mitosis. First: appearance of cyclin B, then
activation of cyclin B (mitosis). When Cyclin B1 disappears → mitosis stops and G1 phase is induced.