04.10.19
L1 – Introduction and Basic concepts
Keywords:
Senescence, hormone (a chemical messenger produced and secreted by a specialized
endocrine gland that is transported in the bloodstream to a distant target organ/cell where
it elicits a physiological response), gland (collection of specialized secretary cells), endocrine
(ductless gland secreting hormones into the blood), exocrine (secretes substances into a
system of ducts), extracellular signaling molecules (collective term for hormones,
neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, GF and cytokines), paracrine/autocrine, lipophilic
Lecture:
Endocrine vs nervous system (neuroendocrine)
o Communication (homeostasis)
o E (mobile phone – no physical connection) & nervous (land-line phone – physical)
o N = rapid, short duration and rapidly ends, E = slow, long duration and slowly
dissociates
Endocrine
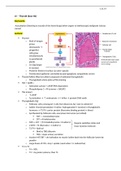
o Arenal glands = cortisol = stress hormone
o Hormones
If local = paracrine/autocrine
Inhib/excitatory Adjacent
o In neuroendocrine
Neurotransmitters pass into blood
to reach target cell
3 classes of hormones
o Proteins/peptides (hydrophilic – doesn’t
require binding partner ؞broken down)
Growth factors
Eg: thyrotrophin-releasing
hormone (from hypothalamus)
w/ 3AAs to TSH w/ 200AAs
Eg insulin from cleaved
precursor preinsulin
Usually formed in intestines
Shorter half-life bc broken down by proteolytic enzymes in blood (no
protection by binding partners)
Most stored in granules Endocrine – distant target cell.
Lipophobic ؞cannot cross Autocrine – same cell.
membranes ؞can be stored in vesicles Paracrine – local cells.
(rapid release) and require Neuroendocrine – nerve cell secretes a
extracellular receptor ligand that travels in the blood to a
o Cholesterol derivatives (hydrophobic – fats, distant target cell.
Lipophilic – lipid soluble) Neurotransmitter – nerve cell secretes
Steroids/vit D a ligand that acts on a local nerve cell.
↑ SER
Eg: cortisol, testosterone and progestogen
L1 – Introduction and Basic concepts
Keywords:
Senescence, hormone (a chemical messenger produced and secreted by a specialized
endocrine gland that is transported in the bloodstream to a distant target organ/cell where
it elicits a physiological response), gland (collection of specialized secretary cells), endocrine
(ductless gland secreting hormones into the blood), exocrine (secretes substances into a
system of ducts), extracellular signaling molecules (collective term for hormones,
neurotransmitters, neuromodulators, GF and cytokines), paracrine/autocrine, lipophilic
Lecture:
Endocrine vs nervous system (neuroendocrine)
o Communication (homeostasis)
o E (mobile phone – no physical connection) & nervous (land-line phone – physical)
o N = rapid, short duration and rapidly ends, E = slow, long duration and slowly
dissociates
Endocrine
o Arenal glands = cortisol = stress hormone
o Hormones
If local = paracrine/autocrine
Inhib/excitatory Adjacent
o In neuroendocrine
Neurotransmitters pass into blood
to reach target cell
3 classes of hormones
o Proteins/peptides (hydrophilic – doesn’t
require binding partner ؞broken down)
Growth factors
Eg: thyrotrophin-releasing
hormone (from hypothalamus)
w/ 3AAs to TSH w/ 200AAs
Eg insulin from cleaved
precursor preinsulin
Usually formed in intestines
Shorter half-life bc broken down by proteolytic enzymes in blood (no
protection by binding partners)
Most stored in granules Endocrine – distant target cell.
Lipophobic ؞cannot cross Autocrine – same cell.
membranes ؞can be stored in vesicles Paracrine – local cells.
(rapid release) and require Neuroendocrine – nerve cell secretes a
extracellular receptor ligand that travels in the blood to a
o Cholesterol derivatives (hydrophobic – fats, distant target cell.
Lipophilic – lipid soluble) Neurotransmitter – nerve cell secretes
Steroids/vit D a ligand that acts on a local nerve cell.
↑ SER
Eg: cortisol, testosterone and progestogen