Intro : Macro Concepts
1. What is the difference between a government “deficit” and a government
“debt”?
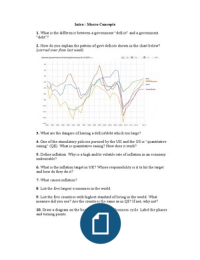
2. How do you explain the pattern of govt deficits shown in the chart below?
(carried over from last week)
3. What are the dangers of having a deficit/debt which too large?
4. One of the stimulatory policies pursued by the UK and the US is “quantitative
easing” (QE). What is quantitative easing? How does it work?
5. Define inflation. Why is a high and/or volatile rate of inflation in an economy
undesirable?
6. What is the inflation target in UK? Whose responsibility is it to hit the target
and how do they do it?
7. What causes inflation?
8. List the five largest economies in the world.
9. List the five countries with highest standard of living in the world. What
measure did you use? Are the countries the same as in Q8? If not, why not?
10. Draw a diagram on the board illustrating the business cycle. Label the phases
and turning points.
1. What is the difference between a government “deficit” and a government
“debt”?
2. How do you explain the pattern of govt deficits shown in the chart below?
(carried over from last week)
3. What are the dangers of having a deficit/debt which too large?
4. One of the stimulatory policies pursued by the UK and the US is “quantitative
easing” (QE). What is quantitative easing? How does it work?
5. Define inflation. Why is a high and/or volatile rate of inflation in an economy
undesirable?
6. What is the inflation target in UK? Whose responsibility is it to hit the target
and how do they do it?
7. What causes inflation?
8. List the five largest economies in the world.
9. List the five countries with highest standard of living in the world. What
measure did you use? Are the countries the same as in Q8? If not, why not?
10. Draw a diagram on the board illustrating the business cycle. Label the phases
and turning points.