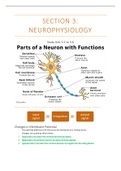
SECTION 3:
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
Study Unit 3.1 to 3.6
Action potentials, or nerve impulses, are electrical impulses carried along the length of axons
input output
integration
signal signal
Changes in Membrane Potential
- The potential difference (70 mV) across the membrane of a resting neuron
- Changes are caused by three events:
1. Depolarization, the inside of the membrane becomes less negative
2. Repolarization, the membrane returns to its resting membrane potential
3. Hyperpolarization, the inside of the membrane becomes more negative than the resting potential
,Action Potential Stages: Overview
,
, Frequency of action potentials
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Tissue
Nervous system
The master controlling and communicating system of the body
Functions
- Act as sensory input monitoring stimuli occurring inside and outside the body
- Responsible for the integration and interpretation of sensory input
- Responsible for motor output response to stimuli by activating effector organs
Afferent and Efferent CNS connections
Sensory signs Motor NS
Afferent Efferent
CNS
Visceral/Autonomic
sensors Autonomic NS
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
Study Unit 3.1 to 3.6
Action potentials, or nerve impulses, are electrical impulses carried along the length of axons
input output
integration
signal signal
Changes in Membrane Potential
- The potential difference (70 mV) across the membrane of a resting neuron
- Changes are caused by three events:
1. Depolarization, the inside of the membrane becomes less negative
2. Repolarization, the membrane returns to its resting membrane potential
3. Hyperpolarization, the inside of the membrane becomes more negative than the resting potential
,Action Potential Stages: Overview
,
, Frequency of action potentials
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Tissue
Nervous system
The master controlling and communicating system of the body
Functions
- Act as sensory input monitoring stimuli occurring inside and outside the body
- Responsible for the integration and interpretation of sensory input
- Responsible for motor output response to stimuli by activating effector organs
Afferent and Efferent CNS connections
Sensory signs Motor NS
Afferent Efferent
CNS
Visceral/Autonomic
sensors Autonomic NS