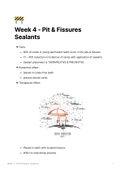
Jeremy Bentham and Act utilitarianism
A teleological theory (Looks at the consequences of an action.)
Utility-the usefulness of actions.
Bentham’s act utilitarianism takes a Other points about act utilitarianism:
teleological approach believing morality o It’s not about your own happiness:
should be based on consequences of Bentham believed that moral agents
actions. should do actions that create more
o The one guiding principle of act pleasure than pain even if it means their
utilitarianism according to Bentham own unhappiness.
was ‘the principle of utility’ ‘every day will invite you to add
Principle of utility: something to the pleasure of others ‘
o Bentham claimed the principle of o Bentham argued that moral agents should
utility is based on the saying of joseph create more pleasure than pain even up
priestly ‘greatest happiness for the to their own death.
greatest number’. o Negative act utilitarianism: what you
o The principle of utility is based heavily should do if all possible actions bring
on Priestley’s saying. The principle more pain. Bentham argued that you
states the morality of any action choose the course of action that creates
should be judged on whether it the least pain.
promotes a balance of pleasure. o Quantity of happiness: Bentham largely
over pain. believed in the quantity of happiness as
o Moral acts-maximise pleasure and opposed to quality. He didn’t care about
minimise pain and vice versa for
immoral acts.
, Hedonism
o He was concerned with social and legal reform
and wanted to develop an ethical theory Hedonic calcus
establishing whether something was good or o Purity-how free from pain is
bad according to its benefit for the majority of it?
the people. o Remoteness-how near is it?
o Hedonism-Bentham’s theory was about o Richness-to what extent will
equating happiness with pleasure and the it lead to other pleasures?
absence of pain which was an empirical o Intensity-how powerful is it?
observation. o Certainty-how likely is it to
o His theory led to extensive social reform result in pleasure?
affecting parliament, criminal law, the jury o Extent-how many people
system, prisons, saving banks etc. does it effect?
His law resulted in all people being considered o Duration-how long will it last?
when making laws. his hedonic calcus was
helpful in determining how to measure
different amounts of pleasure and action
produced.
o It shows that we have to do the pleasure that
creates the biggest gap between pleasure and
A teleological theory (Looks at the consequences of an action.)
Utility-the usefulness of actions.
Bentham’s act utilitarianism takes a Other points about act utilitarianism:
teleological approach believing morality o It’s not about your own happiness:
should be based on consequences of Bentham believed that moral agents
actions. should do actions that create more
o The one guiding principle of act pleasure than pain even if it means their
utilitarianism according to Bentham own unhappiness.
was ‘the principle of utility’ ‘every day will invite you to add
Principle of utility: something to the pleasure of others ‘
o Bentham claimed the principle of o Bentham argued that moral agents should
utility is based on the saying of joseph create more pleasure than pain even up
priestly ‘greatest happiness for the to their own death.
greatest number’. o Negative act utilitarianism: what you
o The principle of utility is based heavily should do if all possible actions bring
on Priestley’s saying. The principle more pain. Bentham argued that you
states the morality of any action choose the course of action that creates
should be judged on whether it the least pain.
promotes a balance of pleasure. o Quantity of happiness: Bentham largely
over pain. believed in the quantity of happiness as
o Moral acts-maximise pleasure and opposed to quality. He didn’t care about
minimise pain and vice versa for
immoral acts.
, Hedonism
o He was concerned with social and legal reform
and wanted to develop an ethical theory Hedonic calcus
establishing whether something was good or o Purity-how free from pain is
bad according to its benefit for the majority of it?
the people. o Remoteness-how near is it?
o Hedonism-Bentham’s theory was about o Richness-to what extent will
equating happiness with pleasure and the it lead to other pleasures?
absence of pain which was an empirical o Intensity-how powerful is it?
observation. o Certainty-how likely is it to
o His theory led to extensive social reform result in pleasure?
affecting parliament, criminal law, the jury o Extent-how many people
system, prisons, saving banks etc. does it effect?
His law resulted in all people being considered o Duration-how long will it last?
when making laws. his hedonic calcus was
helpful in determining how to measure
different amounts of pleasure and action
produced.
o It shows that we have to do the pleasure that
creates the biggest gap between pleasure and