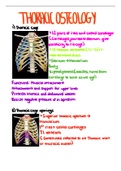
THORACIC OSTEOLOGY
1 Thoracic
cage
I 2 pairs of ribs and costal cartilages
cartilagesjoin ribs to sternum give
elasticity to ribcage
12thoracic vertebrae CT I T 2 t
intervertebral discs
Sternum Manubrium
Body
XiphoidprocessCossifes turns from
cartilage to bone as we
age
Functions Muscle attachment
Attachment and support for upper limb
Protects thoracic andabdominal viscera
Resist negativepressure of inspiration
B Thoraciccageopenings
Superior thoracic aperture
Manubrium
1st ribs t costal cartilages
1 1 vertebra
sometimes referred to as Thoracic inlet
or thoracic outlet
, Inferior thoracic aperture
Xiphoid process
Costa1 margin cartilage of 7 I2
I 1 and 12th ribs
T 12 Vere bra
Because the diaphragm moves upwards
many abdominal
organs are protected by the thoraciccage
Clinical context Thoracic outlet syndrome
Compression of structures passing from the superior
thoracic apehere to the axilla
Obstructions Nerves brachialplexus vessels subclavia
artery or vein passing to the upper limb
Symptoms Weakness pain1 numbness I altered sensation
of upper limb If vessels are compressedyou see swelling
may
reduced blood pressure in that arm claudication pain upon
exertion due to lack of blood flow clots
Causes A cervical rib or anamdous first rib
Compressionbetween musclesCscalenes
Rib 1 clavicle fracture
Inflammation from repetitiveoverhead movement
1 Thoracic
cage
I 2 pairs of ribs and costal cartilages
cartilagesjoin ribs to sternum give
elasticity to ribcage
12thoracic vertebrae CT I T 2 t
intervertebral discs
Sternum Manubrium
Body
XiphoidprocessCossifes turns from
cartilage to bone as we
age
Functions Muscle attachment
Attachment and support for upper limb
Protects thoracic andabdominal viscera
Resist negativepressure of inspiration
B Thoraciccageopenings
Superior thoracic aperture
Manubrium
1st ribs t costal cartilages
1 1 vertebra
sometimes referred to as Thoracic inlet
or thoracic outlet
, Inferior thoracic aperture
Xiphoid process
Costa1 margin cartilage of 7 I2
I 1 and 12th ribs
T 12 Vere bra
Because the diaphragm moves upwards
many abdominal
organs are protected by the thoraciccage
Clinical context Thoracic outlet syndrome
Compression of structures passing from the superior
thoracic apehere to the axilla
Obstructions Nerves brachialplexus vessels subclavia
artery or vein passing to the upper limb
Symptoms Weakness pain1 numbness I altered sensation
of upper limb If vessels are compressedyou see swelling
may
reduced blood pressure in that arm claudication pain upon
exertion due to lack of blood flow clots
Causes A cervical rib or anamdous first rib
Compressionbetween musclesCscalenes
Rib 1 clavicle fracture
Inflammation from repetitiveoverhead movement