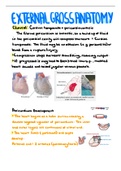
EXTERNAL GROSS ANATOMY
Clinical Cardiactamponade t pericardiocentesis
The fibrous pericardium is inelastic so a buildup of fluid
in thepericardialcavity will compress the heart Cardiac
tamponade The fluid may be an effusion Ce g pericarditis or
blood from a rupture injury
Compression stops the heart from filling reducing output
If progressed it may lead to Beck's triad low b p muffled
heart sounds and raised jugular venous pressure
Pericardium Development
The heart begins as a tube surrounded
by a
double layeredcylinder of pericardium The inner
and outer layers are continuous at either end
The heart folds partitions and Septa
develop
Arterial end 2 arteries pulmonary1 aorta
, Venous end 6 veins CNC SVC 4 x
pulmonary
Pericardial sinuses
Due to development there are two pericardial sinuses The
Transverse and oblique sinuses
Posterior to aorta t Posterior to heart
Pulmonary trunk near
pulmonaryveins
and IVC where visceral
pericardium reflects to
become parietal It over
lies the oesophagus
Clinical Cardiactamponade t pericardiocentesis
The fibrous pericardium is inelastic so a buildup of fluid
in thepericardialcavity will compress the heart Cardiac
tamponade The fluid may be an effusion Ce g pericarditis or
blood from a rupture injury
Compression stops the heart from filling reducing output
If progressed it may lead to Beck's triad low b p muffled
heart sounds and raised jugular venous pressure
Pericardium Development
The heart begins as a tube surrounded
by a
double layeredcylinder of pericardium The inner
and outer layers are continuous at either end
The heart folds partitions and Septa
develop
Arterial end 2 arteries pulmonary1 aorta
, Venous end 6 veins CNC SVC 4 x
pulmonary
Pericardial sinuses
Due to development there are two pericardial sinuses The
Transverse and oblique sinuses
Posterior to aorta t Posterior to heart
Pulmonary trunk near
pulmonaryveins
and IVC where visceral
pericardium reflects to
become parietal It over
lies the oesophagus