Unit 8: physiology of the human body systems
Learning aim a: Understand the impact of disorders of the
musculoskeletal system and their associated corrective treatments
Title: musculoskeletal system
aims:
1) Fully evaluate the effectiveness, limitations, strengths and weaknesses of
various corrective actions and alternative treatment methods offered by
medical professionals for one disorder of the musculoskeletal system.
2) Explain the anatomy, physiology, and functional roles of the system.
3) Describe three different musculoskeletal disorders and therefore the
corrective treatments associated with these disorders.
4) Describe and compare the corrective treatment used for each of the three
disorders you have chosen to research.
The musculoskeletal system provides stability ,movement and form. The bones, cartilage,
ligaments, tendons and connective tissues are included in the musculoskeletal system. A
structure for the muscles and other soft tissues is given by the skeleton. They collectively
support the body's weight, maintain balance and help the body to function. the
musculoskeletal system, has a wide spectrum of disorders and conditions which
could lead to complications such as Ageing, incidents, genetic malformations (birth
defects) and illness which can cause discomfort and restrict movement.
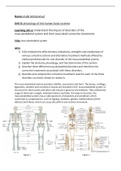
Figure 1. Figure 2
,Axial skeleton Appendicular skeleton
The axial skeleton is located in the central axis of The appendicular skeleton is connected to the
the body. It consists of 6 main regions , skull, centre axis from the shoulder girdle and pelvic
ossicles , hyoid , vertebral column , sternum and girdle. There are 6 main regions the shoulder, arm ,
the rib cage. Those 6 parts are made up of 80 bones hand , pelvis , leg and foot. From these regions
the skull consists of 22 bones 14 of which are facial there are 126 bones that are functionally involved
and 8 are cranial. There is 1 hyoid bone; 26 in manipulation of objects in the environment and
vertebral column; 1 sternum bone; 6 ossicles and locomotion of the upper and lower limbs.
24 rib bones.
Support in the body
Bones: Bones sustain the body in all forms and sizes, defend organs and tissues, store
calcium and fat and create cells in the blood. The rigid outer layer of a bone covers a
spongy core. For the body, bones have shape and shape. To make you travel, they work
through muscles, tendons, ligaments and other connective tissues.
1. Flat bones: are mostly located in the axial skeletal and its function protect internal
organs and consist of , cranial bones that protect the brain ; sternum and rib
bones that protect the heart and lungs. Flat bones have a large surface area for
muscles to attach and are flat to act like shielding.
, 2. Long bones: Most of them are found in the appendicular skeleton and their
purpose is to transfer and maintain the upper and lower limbs' weight and
movement. They are broader than broad and contain the femur, the longest bone
in the body.
3. Short bones: are located in the ankle (tarsals) and wrist (carpals) joints to provide
some movement and stability. Short bones are cube shaped and it’s length and
it’s width are directly proportional.