Chapter 15: Adrenergic Agonists and Antagonists
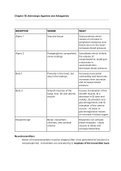
RECEPTOR WHERE WHAT
Alpha 1 Vascular tissue Vasoconstricts which
causes an increase in
peripheral resistance and
blood return to the heart -
increases blood pressure
Alpha 2 Postganglionic sympathetic Vasodilates which inhibits
nerve endings the release of
norepinephrine, leading to
a decrease in
vasoconstriction -
decreases blood pressure
Beta 1 Primarily in the heart, but Increases myocardial
also in the kidneys contractility and heart rate -
increases renin secretion
and increases blood
pressure
Beta 2 Smooth muscles of the Causes 1) relaxation of the
lungs, liver, GI, and uterine smooth muscle, 2) a
muscle decrease in GI tone and
motility, 3) activation and
gluconeogenesis, and 4)
relaxation of the uterine
muscle - increase in
gluconeogenesis causes
an increase in blood sugars
Dopaminergic Renal, mesenteric, Dopamine can activate
coronary, and cerebral these receptors - cause
arteries vessels to dilate and
increase blood flow
Neurotransmitters
- Action of neurotransmitters must be stopped after it has performed its function (i.e.
norepinephrine) - transmitters are activated by 1) reuptake of the transmitter back
, into the neuron, 2) enzymatic transformation or degradation, and 3) diffusion
away from the receptor
- 2 ENZYMES THAT INACTIVATE NOREPINEPHRINE
- 1) monoamine oxidase (MAO): inside the neuron
- 2) catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT): outside the neuron
- *Think antidepressants* MAO inhibit the reuptake of dopamine so that dopamine
is continually circulating, rather than going through reuptake - clients with
depression have less dopamine circulating - want to preserve the little that is
available by inhibiting reuptake
Sympathomimetics
- These are drugs are classified by how they affect an organ cell
- a) Direct-acting sympathomimetic
- Directly stimulates the adrenergic receptor - an example would be
norepinephrine and epinephrine
- b) indirect-acting sympathomimetic
- Stimulates the release of norepinephrine from the terminal nerve
endings - an example would be amphetamine
- c) mixed-acting sympathomimetic
- Stimulates the adrenergic receptor sites and stimulate the release of
norepinephrine from the terminal nerve endings - an example would
be pseudoephedrine - acts indirectly by stimulating the release of
norepinephrine from the nerve terminals and acts directly on the
alpha 1 and beta 1 receptors - increases heart rate - not as potent
and there is less risk of hemorrhagic stroke and hypertensive crisis.
, Catecholamines
- Chemical structures of a substance that can produce a sympathomimetic
response
- Endogenous catecholamines: epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine
- Synthetic catecholamines: isoproterenol and dobutamine
- Noncatecholamines stimulate the adrenergic receptors - have a longer duration of
action than the endogenous or synthetic catecholamines
Adrenergic Blockers (Antagonists)
- Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers: selective and non-selective - many of these drugs are
not frequently prescribed as beta blockers because it causes orthostatic
hypotension
- Alpha blockers promote vasodilation, low blood pressure, increased heart
rate - inhibiting what alpha 1 and alpha 2 receptors USUALLY do - these are
usually used for patients with peripheral vascular disease such as
Raynaud’s disease
- Beta-Adrenergic Blockers: selective & also non-selective by blocking both beta 1
and beta 2 receptors - causes a decrease in blood pressure and decrease in
heart rate - ALSO CAUSES BRONCHOCONSTRICTION - *be very cautious when
giving beta blockers to patients with COPD or asthma as it can cause even further
bronchoconstriction*
- An example of a non-selective beta blocker is Propranolol - treats angina,
cardiac dysrhythmias, hypertension and heart failure - has many side
effects because it is non-selective
- Selective adrenergic blocker have a greater affinity for certain receptors -
target a certain problem such as high heart rate or high blood pressure -
target beta 1 or beta 2 - an example of beta 1 blocker is atenolol and
metoprolol
- Intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) is the ability of certain beta blockers to
bind with a beta receptor to prevent strong agonists from binding to that receptor
producing complete activation
- Nonselective beta blockers that have ISA: carteolol, carvedilol, penbutolol,
pindolol
- Selective beta blockers that have ISA: acebutolol
Adrenergic Neuron Blockers
RECEPTOR WHERE WHAT
Alpha 1 Vascular tissue Vasoconstricts which
causes an increase in
peripheral resistance and
blood return to the heart -
increases blood pressure
Alpha 2 Postganglionic sympathetic Vasodilates which inhibits
nerve endings the release of
norepinephrine, leading to
a decrease in
vasoconstriction -
decreases blood pressure
Beta 1 Primarily in the heart, but Increases myocardial
also in the kidneys contractility and heart rate -
increases renin secretion
and increases blood
pressure
Beta 2 Smooth muscles of the Causes 1) relaxation of the
lungs, liver, GI, and uterine smooth muscle, 2) a
muscle decrease in GI tone and
motility, 3) activation and
gluconeogenesis, and 4)
relaxation of the uterine
muscle - increase in
gluconeogenesis causes
an increase in blood sugars
Dopaminergic Renal, mesenteric, Dopamine can activate
coronary, and cerebral these receptors - cause
arteries vessels to dilate and
increase blood flow
Neurotransmitters
- Action of neurotransmitters must be stopped after it has performed its function (i.e.
norepinephrine) - transmitters are activated by 1) reuptake of the transmitter back
, into the neuron, 2) enzymatic transformation or degradation, and 3) diffusion
away from the receptor
- 2 ENZYMES THAT INACTIVATE NOREPINEPHRINE
- 1) monoamine oxidase (MAO): inside the neuron
- 2) catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT): outside the neuron
- *Think antidepressants* MAO inhibit the reuptake of dopamine so that dopamine
is continually circulating, rather than going through reuptake - clients with
depression have less dopamine circulating - want to preserve the little that is
available by inhibiting reuptake
Sympathomimetics
- These are drugs are classified by how they affect an organ cell
- a) Direct-acting sympathomimetic
- Directly stimulates the adrenergic receptor - an example would be
norepinephrine and epinephrine
- b) indirect-acting sympathomimetic
- Stimulates the release of norepinephrine from the terminal nerve
endings - an example would be amphetamine
- c) mixed-acting sympathomimetic
- Stimulates the adrenergic receptor sites and stimulate the release of
norepinephrine from the terminal nerve endings - an example would
be pseudoephedrine - acts indirectly by stimulating the release of
norepinephrine from the nerve terminals and acts directly on the
alpha 1 and beta 1 receptors - increases heart rate - not as potent
and there is less risk of hemorrhagic stroke and hypertensive crisis.
, Catecholamines
- Chemical structures of a substance that can produce a sympathomimetic
response
- Endogenous catecholamines: epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine
- Synthetic catecholamines: isoproterenol and dobutamine
- Noncatecholamines stimulate the adrenergic receptors - have a longer duration of
action than the endogenous or synthetic catecholamines
Adrenergic Blockers (Antagonists)
- Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers: selective and non-selective - many of these drugs are
not frequently prescribed as beta blockers because it causes orthostatic
hypotension
- Alpha blockers promote vasodilation, low blood pressure, increased heart
rate - inhibiting what alpha 1 and alpha 2 receptors USUALLY do - these are
usually used for patients with peripheral vascular disease such as
Raynaud’s disease
- Beta-Adrenergic Blockers: selective & also non-selective by blocking both beta 1
and beta 2 receptors - causes a decrease in blood pressure and decrease in
heart rate - ALSO CAUSES BRONCHOCONSTRICTION - *be very cautious when
giving beta blockers to patients with COPD or asthma as it can cause even further
bronchoconstriction*
- An example of a non-selective beta blocker is Propranolol - treats angina,
cardiac dysrhythmias, hypertension and heart failure - has many side
effects because it is non-selective
- Selective adrenergic blocker have a greater affinity for certain receptors -
target a certain problem such as high heart rate or high blood pressure -
target beta 1 or beta 2 - an example of beta 1 blocker is atenolol and
metoprolol
- Intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) is the ability of certain beta blockers to
bind with a beta receptor to prevent strong agonists from binding to that receptor
producing complete activation
- Nonselective beta blockers that have ISA: carteolol, carvedilol, penbutolol,
pindolol
- Selective beta blockers that have ISA: acebutolol
Adrenergic Neuron Blockers