Quiz # 1 Study Guide
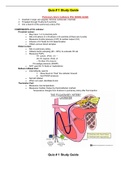
Pulmonary Artery Catheters (PA) (SWAN-GANZ)
1. Inserted in large vein (jugular, femoral, subclavian, brachial)
2. Threated through R-atria & R-ventricle
3. Into a branch of the pulmonary artery (PA)
COMPONENTS of PA catheter:
Proximal Lumen:
o May have 1 or 2 proximal ports
o Sits in R-atrium or in R-atrium or R-ventricle (if there are 2 ports)
o Measures R-atria pressure (CVP) & cardiac output (CO)
o Infusion of IV fluids for CO determination
o Obtain venous blood samples
Distal Lumen:
o Sits in pulmonary artery
o Obtains SvO2 sampling (60 – 80%) to evaluate O2 sat
o Measures PAPs:
PA systolic (PAS) (15 –
28) PA diastolic (PAD) (5
– 16) Mean PA pressure
PA wedge pressure (PAWP)
o NOT used for IV fluids or medications
Balloon Inflated Port:
o Intermittently used to
1. Allow blood to “float” the catheter forward
2. Get PAWP pressure
o Not left inflated
o When not used, disinflate & lock
Thermistor Port:
o Measures core temperature
o Measures Cardiac Output by thermodilution method
Temperature changes from R-atrium to pulmonary artery after fluid injection
Quiz # 1 Study Guide
, INDICATIONS:
Serious or critical
illness Heart failure
Post coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) clients
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Acute kidney
injury Burn injury
Trauma injury
POCEDURE PROCESS:
PRE-PROCEDURE:
o Ensure understanding of procedure prior to informed consent
o Assemble the pressure monitoring system. Purge air from the system and maintain
sterility of connections.
o Place in supine or Trendelenburg position.
o Administer sedation and pain medications
o Level transducer with phlebostatic axis (4th intercostal space, midaxillary line)
(corresponds with the R-atrium)
o Zero system with atmospheric pressure
DURING:
o Monitor for manifestations altered hemodynamics
o Watch waveform as catheter is threated
o Monitor EKG for dysrhythmias and SpO2 for desaturation
Initial catheter placement in central vein can result in pneumothorax
Catheter movement through heart can cause irritability of heart cells
leading to dysrhythmias
POST-PROCEDURE:
o Chest X-Ray to confirm placement
o Assess respiratory & cardiac status (vitals, heart rhythm,
SaO2) Auscultate lung sounds (pattern & effort)
Compare arterial blood pressure to noninvasive blood pressure (NIBP)
o Maintain line placement and integrity
Observe & document initial waveform readings & response (changes can indicate
catheter migration or displacement) (document catheter placement each shift)
Monitor and secure catheter connections
Quiz # 1 Study Guide
COMPLICATIONS:
During Inserting
o Arterial puncture
o Pneumothorax
o Dysrhythmias
o Introduction of air emboli
Pulmonary Artery Catheters (PA) (SWAN-GANZ)
1. Inserted in large vein (jugular, femoral, subclavian, brachial)
2. Threated through R-atria & R-ventricle
3. Into a branch of the pulmonary artery (PA)
COMPONENTS of PA catheter:
Proximal Lumen:
o May have 1 or 2 proximal ports
o Sits in R-atrium or in R-atrium or R-ventricle (if there are 2 ports)
o Measures R-atria pressure (CVP) & cardiac output (CO)
o Infusion of IV fluids for CO determination
o Obtain venous blood samples
Distal Lumen:
o Sits in pulmonary artery
o Obtains SvO2 sampling (60 – 80%) to evaluate O2 sat
o Measures PAPs:
PA systolic (PAS) (15 –
28) PA diastolic (PAD) (5
– 16) Mean PA pressure
PA wedge pressure (PAWP)
o NOT used for IV fluids or medications
Balloon Inflated Port:
o Intermittently used to
1. Allow blood to “float” the catheter forward
2. Get PAWP pressure
o Not left inflated
o When not used, disinflate & lock
Thermistor Port:
o Measures core temperature
o Measures Cardiac Output by thermodilution method
Temperature changes from R-atrium to pulmonary artery after fluid injection
Quiz # 1 Study Guide
, INDICATIONS:
Serious or critical
illness Heart failure
Post coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) clients
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Acute kidney
injury Burn injury
Trauma injury
POCEDURE PROCESS:
PRE-PROCEDURE:
o Ensure understanding of procedure prior to informed consent
o Assemble the pressure monitoring system. Purge air from the system and maintain
sterility of connections.
o Place in supine or Trendelenburg position.
o Administer sedation and pain medications
o Level transducer with phlebostatic axis (4th intercostal space, midaxillary line)
(corresponds with the R-atrium)
o Zero system with atmospheric pressure
DURING:
o Monitor for manifestations altered hemodynamics
o Watch waveform as catheter is threated
o Monitor EKG for dysrhythmias and SpO2 for desaturation
Initial catheter placement in central vein can result in pneumothorax
Catheter movement through heart can cause irritability of heart cells
leading to dysrhythmias
POST-PROCEDURE:
o Chest X-Ray to confirm placement
o Assess respiratory & cardiac status (vitals, heart rhythm,
SaO2) Auscultate lung sounds (pattern & effort)
Compare arterial blood pressure to noninvasive blood pressure (NIBP)
o Maintain line placement and integrity
Observe & document initial waveform readings & response (changes can indicate
catheter migration or displacement) (document catheter placement each shift)
Monitor and secure catheter connections
Quiz # 1 Study Guide
COMPLICATIONS:
During Inserting
o Arterial puncture
o Pneumothorax
o Dysrhythmias
o Introduction of air emboli