Blood [Glucose]:
- Random: <10 mmol/L
- Fasting 3.5-5.5 mmol/L
- Essential for brain function
- Regulation via insulin and glucagon
Functions of insulin:
1. Stimulatory
a. Glucose uptake by muscle / adipose
b. Glycolysis
c. Glycogen synthesis
d. Protein synthesis
e. Cellular uptake of potassium / phosphate
2. Inhibitory:
a. Gluconeogenesis
b. Glycogenolysis
c. Ketogenesis
d. Proteolysis
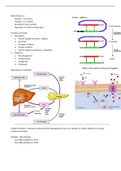
Blood Glucose regulation:
Diabetes Mellitus: a syndrome characterised by hyperglycemia due to an absolute or relative deficiency of and/or
resistance to insulin
Diabetes - IDF estimates:
- 422 million diabetics in 2014
- 592 million diabetics in 2035
- Random: <10 mmol/L
- Fasting 3.5-5.5 mmol/L
- Essential for brain function
- Regulation via insulin and glucagon
Functions of insulin:
1. Stimulatory
a. Glucose uptake by muscle / adipose
b. Glycolysis
c. Glycogen synthesis
d. Protein synthesis
e. Cellular uptake of potassium / phosphate
2. Inhibitory:
a. Gluconeogenesis
b. Glycogenolysis
c. Ketogenesis
d. Proteolysis
Blood Glucose regulation:
Diabetes Mellitus: a syndrome characterised by hyperglycemia due to an absolute or relative deficiency of and/or
resistance to insulin
Diabetes - IDF estimates:
- 422 million diabetics in 2014
- 592 million diabetics in 2035