Unit 11 assignment 1
Task 1
Acinar cells are stored in the pancreas and are used to synthesize, secrete and store digestive
enzymes for use within the small intestine.
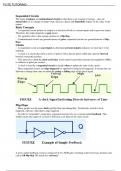
This is a acinar cell from the human pancreas including labelled organelles:
, Unit 11 assignment 1
Roles of organelles within an acinar cell:
Ribosomes
Ribosomes consist of two subunits which are suitably composed and function as one to
translate the mRNA into a polypeptide chain during protein
synthesis. This is the site of protein synthesis (where
proteins are made). Therefore - the function of ribosomes is
to synthesize proteins as directed in the messenger RNA.
Protein is needed for many cell functions such as repairing
damage or directing chemical processes.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria is a membrane-bound organelle located in the cytoplasm of almost all eukaryotic
cells. It is the powerhouse of the cell as its main function is to generate large quantities of
energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP. This is made through cellular
respiration. This is where it takes in nutrients from the cell, breaks it down, and turns it into
energy. This energy is then in turn used by the cell to carry
out various functions. Mitochondria are usually round to
oval in shape and range in size from 0.5 to 10 μm. They
store calcium for cell signaling activities, generate heat,
and mediate cell growth and death also.It has two
membranes, an outer membrane and an inner membrane.
The folds increase the surface area of the membrane,
which is important because the inner membrane holds
proteins.
Golgi apparatus
Golgi apparatus was discovered in the year 1898 by biologist Camillo Golgi. It was one of the
first cellular organelles to be discovered and observed in detail due
to its large size. The Golgi apparatus can be identified by its unique
structure which looks like a maze, but the structure is made of
stacks of flattened membranous sacs, or cisternae. These
membranes are not connected, like the ones in ER. It collects
simple molecules and combines them to make molecules which
are more complex. It then takes them and packs them in vesicles,
and either stores them for later use or sends them out of the cell. It
is also the organelle that builds lysosomes which is for cell
digestion and is a major site of carbohydrate synthesis.
Task 1
Acinar cells are stored in the pancreas and are used to synthesize, secrete and store digestive
enzymes for use within the small intestine.
This is a acinar cell from the human pancreas including labelled organelles:
, Unit 11 assignment 1
Roles of organelles within an acinar cell:
Ribosomes
Ribosomes consist of two subunits which are suitably composed and function as one to
translate the mRNA into a polypeptide chain during protein
synthesis. This is the site of protein synthesis (where
proteins are made). Therefore - the function of ribosomes is
to synthesize proteins as directed in the messenger RNA.
Protein is needed for many cell functions such as repairing
damage or directing chemical processes.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria is a membrane-bound organelle located in the cytoplasm of almost all eukaryotic
cells. It is the powerhouse of the cell as its main function is to generate large quantities of
energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP. This is made through cellular
respiration. This is where it takes in nutrients from the cell, breaks it down, and turns it into
energy. This energy is then in turn used by the cell to carry
out various functions. Mitochondria are usually round to
oval in shape and range in size from 0.5 to 10 μm. They
store calcium for cell signaling activities, generate heat,
and mediate cell growth and death also.It has two
membranes, an outer membrane and an inner membrane.
The folds increase the surface area of the membrane,
which is important because the inner membrane holds
proteins.
Golgi apparatus
Golgi apparatus was discovered in the year 1898 by biologist Camillo Golgi. It was one of the
first cellular organelles to be discovered and observed in detail due
to its large size. The Golgi apparatus can be identified by its unique
structure which looks like a maze, but the structure is made of
stacks of flattened membranous sacs, or cisternae. These
membranes are not connected, like the ones in ER. It collects
simple molecules and combines them to make molecules which
are more complex. It then takes them and packs them in vesicles,
and either stores them for later use or sends them out of the cell. It
is also the organelle that builds lysosomes which is for cell
digestion and is a major site of carbohydrate synthesis.